| 混凝-超滤工艺处理饮用水厂滤池反冲洗水和排泥水的效能 |
| |
| 引用本文: | 李鼎, 董慧峪, 李海华, 储文斌, 许谦, 蒋才芳, 段书乐, 苗钦奎, 强志民. 混凝-超滤工艺处理饮用水厂滤池反冲洗水和排泥水的效能[J]. 环境工程学报, 2023, 17(10): 3169-3177. doi: 10.12030/j.cjee.202306042 |
| |
| 作者姓名: | 李鼎 董慧峪 李海华 储文斌 许谦 蒋才芳 段书乐 苗钦奎 强志民 |
| |
| 作者单位: | 1.华北水利水电大学环境与市政工程学院,郑州 450046;; 2.中国科学院生态环境研究中心,饮用水科学与技术重点实验室,北京 100085;; 3.浙江工业大学环境学院,杭州 310014;; 4.广西绿城水务股份有限公司,南宁 530029;; 5.南开大学环境科学与工程学院,天津 300350 |
| |
| 基金项目: | 广西绿城水务水厂生产废水处理回用项目(202101),国家自然科学基金面上资助项目(52070184, 52270012)。 |
| |
| 摘 要: | 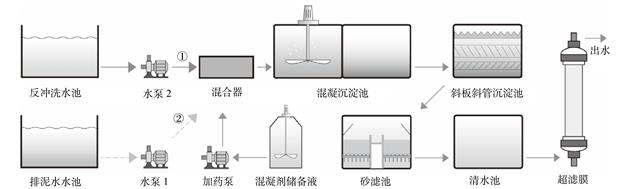
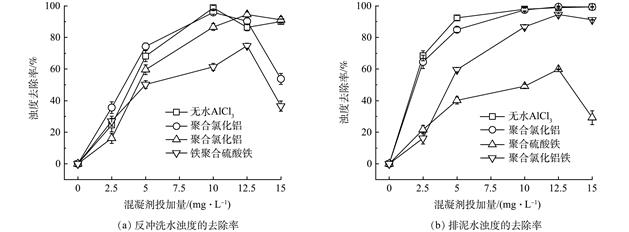
为探究饮用水厂滤池反冲洗水和排泥水的直接回用和处理后回用对水厂的影响及两类水处理过程中的差异,采用了污染负荷计算、实验室混凝小试和现场混凝-超滤中试装置对两类生产废水分别进行了研究。溶解性有机碳(dissolved organic carbon,DOC)、氨氮 (NH4+-N)、Al3+和全氟类化合物(perfluorinated compounds,PFASs)的污染负荷计算结果表明生产废水直接回用会为水厂带来一定的额外负荷,其中排泥水和反冲洗水分别对PFASs和Al3+负荷贡献较大;通过对小试中浊度,UV254以及5种荧光组分去除效果的对比,反冲洗水的混凝效果稍好于排泥水,同时10 mg·L−1的聚合氯化铝为最佳混凝剂方案;在中试过程中,两类水中的浊度、有机物、Al3+和PFASs均可被有效去除,出水差异较小,但反冲洗水中的亲水性和小分子有机物使得其去除效果低于排泥水。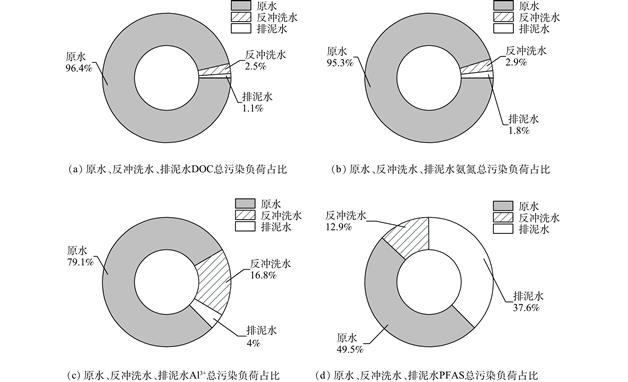
总体来说,经过处理之后,两类生产废水均可回用,回用可有效减少废水排放量,提高水厂水资源利用率。
|
| 关 键 词: | 滤池反冲洗水 沉淀池排泥水 混凝 聚合氯化铝 超滤 |
| 收稿时间: | 2023-06-09 |
|
| 点击此处可从《环境工程学报》浏览原始摘要信息 |
|
点击此处可从《环境工程学报》下载全文 |
|



