| “双碳”目标下污染场地原位热处理技术发展趋势 |
| |
| 引用本文: | 杨洁, 叶春梅, 司马菁珂, 黄沈发, 周栋. “双碳”目标下污染场地原位热处理技术发展趋势[J]. 环境工程学报, 2022, 16(11): 3517-3529. doi: 10.12030/j.cjee.202203006 |
| |
| 作者姓名: | 杨洁 叶春梅 司马菁珂 黄沈发 周栋 |
| |
| 作者单位: | 1.上海市环境科学研究院,上海 200233; 2.国家环境保护城市土壤污染控制与修复工程技术中心,上海 200233 |
| |
| 基金项目: | 国家重点研发计划项目(2019YFC1805702); |
| |
| 摘 要: | 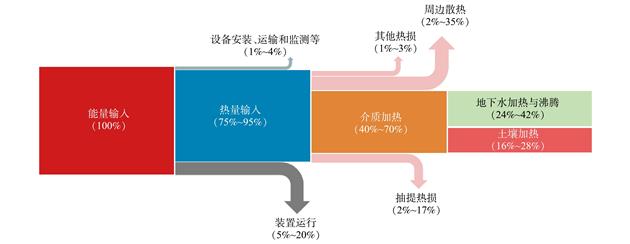
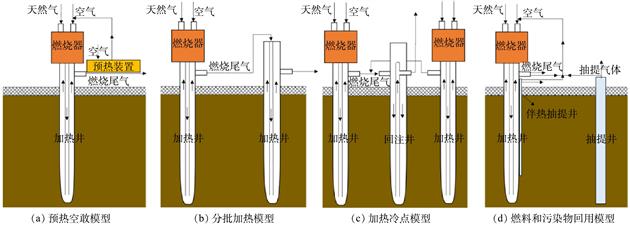
原位热处理技术可以在低地下扰动的前提下实现污染场地快速高效的修复,已成为高浓度挥发/半挥发性有机物污染场地修复的热门技术之一。然而,传统原位热处理技术存在能耗和碳排放较高的弊端,限制了其大范围推广应用。在“碳达峰、碳中和”的战略目标下,亟需开展原位热处理技术的优化研究以降低其能效比。通过国内外实验研究与工程案例的整理分析,识别原位热处理活动中的碳排放和能耗的关键工艺环节,进而提出该技术低碳化发展的主要方向;同时梳理原位热处理工艺中应用再生能源和技术优化的研究进展,展望“双碳”目标下该技术的重点研究方向。目前已获得的研究结果表明,通过应用可再生能源和技术优化有望实现原位热修复工艺的大幅减排。
|
| 关 键 词: | 有机物污染场地 原位热处理技术 碳达峰 碳中和 能耗 碳排放 |
| 收稿时间: | 2022-03-01 |
|
| 点击此处可从《环境工程学报》浏览原始摘要信息 |
|
点击此处可从《环境工程学报》下载全文 |
|


