| TEPA调控AMP-DGDE水溶液相变吸收CO2性能及机理 |
| |
| 引用本文: | 刘超, 王丹, 梁美贞, 周小斌. TEPA调控AMP-DGDE水溶液相变吸收CO2性能及机理[J]. 环境工程学报, 2023, 17(9): 2983-2992. doi: 10.12030/j.cjee.202305103 |
| |
| 作者姓名: | 刘超 王丹 梁美贞 周小斌 |
| |
| 作者单位: | 1.桂林理工大学环境科学与工程学院,桂林 541004;; 2.广西环境污染控制理论与技术重点实验室,桂林 541004;; 3.岩溶地区水污染控制与用水安全保障协同创新中心,桂林 541004 |
| |
| 基金项目: | 国家自然科学基金资助项目(22006027);;广西自然科学基金资助项目(2023GXNSFAA026381); |
| |
| 摘 要: | 
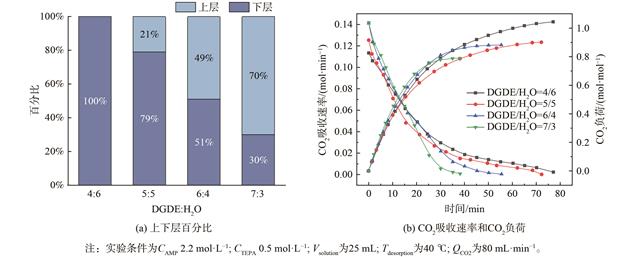
相变吸收剂在降低CO2捕集能耗方面具有较大优势,但现有吸收剂普遍存在再生性能差的问题。基于2-氨基-2-甲基-1-丙醇 (AMP) 的吸收剂再生性能优异,但通常难以发生相变。利用四乙烯五胺 (TEPA) 作为相变调控剂引入AMP-二乙二醇二甲醚 (DGDE) 水溶液,构建了具有良好再生性能的新型相变吸收剂AMP-DGDE-TEPA。在最佳配比下,AMP-DGDE-TEPA的吸收负荷可达0.88 mol∙mol−1,其中97.6%的CO2富集于溶液下层,下层体积仅占总体积51%。经7次吸收-解吸循环,吸收剂的吸收负荷仍能保持0.63 mol∙mol−1,再生效率为71.6%。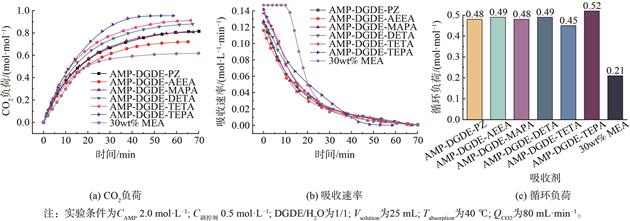
13C核磁共振结果表明,AMP与CO2反应生成易于分解的碳酸氢盐,因而吸收剂具有良好的再生性能;而TEPA的引入可使系统中生成稳定的质子化TEPA和氨基甲酸盐。质子化TEPA和氨基甲酸盐具有高极性,可打破吸收剂原有的均相状态,促使吸收剂发生液-液相变。相比于DGDE,H2O和极性反应产物之间具有更强的相互作用力,这些物质聚集形成CO2富相,而DGDE则单独形成CO2贫相。此外,AMP-DGDE-TEPA的再生显热和潜热仅为0.33和0.43 GJ∙t−1 CO2,具有良好的节能潜力。该研究结果可为高效低能耗碳捕集材料的制备提供参考。
|
| 关 键 词: | CO2捕集 相变吸收剂 2-氨基-2-甲基-1-丙醇 四乙烯五胺 相变机理 |
| 收稿时间: | 2023-05-25 |
|
| 点击此处可从《环境工程学报》浏览原始摘要信息 |
|
点击此处可从《环境工程学报》下载全文 |
|



