| TiO2/UV/O3协同老化对微塑料吸附甲基橙的影响 |
| |
| 引用本文: | 葛建华, 丁雨薇, 吴为, 马东坡, 任雪. TiO2/UV/O3协同老化对微塑料吸附甲基橙的影响[J]. 环境工程学报, 2023, 17(8): 2576-2586. doi: 10.12030/j.cjee.202304004 |
| |
| 作者姓名: | 葛建华 丁雨薇 吴为 马东坡 任雪 |
| |
| 作者单位: | 1.安徽理工大学地球与环境学院,淮南 232001;; 2.安徽省高潜水位矿区水土资源综合利用与生态保护工程实验室,淮南 232001 |
| |
| 基金项目: | 安徽省自然科学基金面上项目(1808085ME139); |
| |
| 摘 要: | 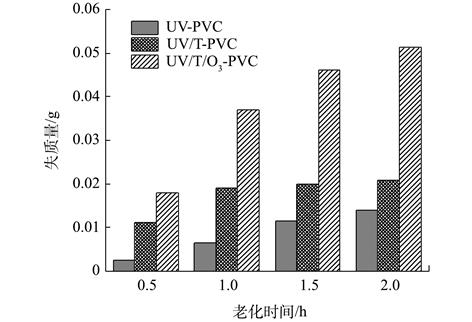
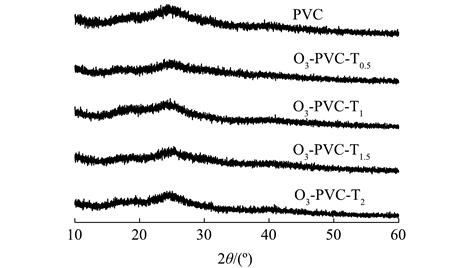
为了探究协同老化后的微塑料与有机污染物的相互作用机制,以PVC作为研究对象,采用TiO2/UV/O3协同老化方式,对比考察了老化前后PVC对甲基橙(MO)的吸附性能。结果表明,随着老化的进行,PVC颗粒表面碎片化加深,粒径明显减小,Zeta电位值降低,并出现了新的含氧官能团。原始PVC对MO的吸附符合准一级动力学模型,而老化后的PVC对MO的吸附符合准二级动力学模型,且主要的吸附模式均为液膜扩散和颗粒内扩散。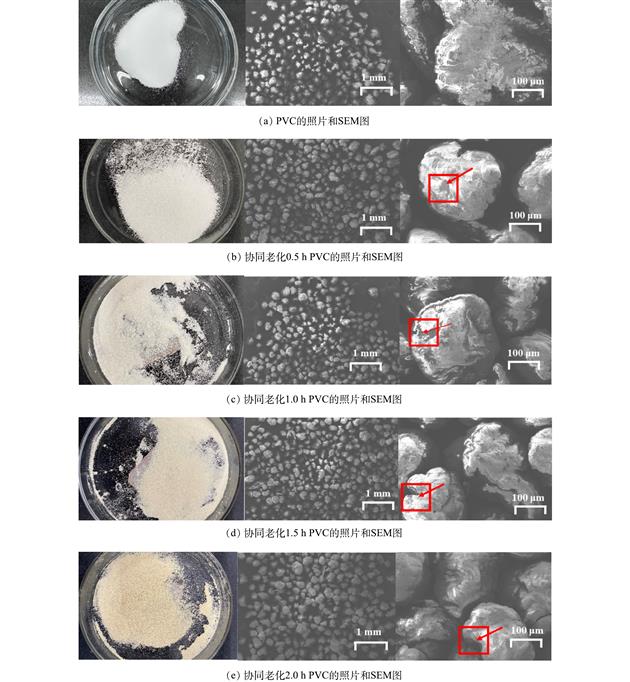
动力学拟合结果表明老化前的PVC对MO的吸附以物理吸附为主,而老化后的PVC对MO的吸附以化学吸附为主。老化前后的PVC对MO的吸附均符合Freundlich等温吸附模型,表明MO与微塑料之间的相互作用是在非均匀表面上的多层吸附。以上研究结果可为微塑料携带有机污染物在环境中的迁移转化的行为提供参考。
|
| 关 键 词: | 微塑料 协同老化 吸附 甲基橙 |
| 收稿时间: | 2023-04-02 |
|
| 点击此处可从《环境工程学报》浏览原始摘要信息 |
|
点击此处可从《环境工程学报》下载全文 |
|



