| 基于碳数分段法的石油烃污染土壤异位热脱附工艺的优化 |
| |
| 引用本文: | 于天, 陈春红, 徐成华, 刘刚, 施威, 洪雅敏, 张亚平. 基于碳数分段法的石油烃污染土壤异位热脱附工艺的优化[J]. 环境工程学报, 2021, 15(6): 1988-1999. doi: 10.12030/j.cjee.202011147 |
| |
| 作者姓名: | 于天 陈春红 徐成华 刘刚 施威 洪雅敏 张亚平 |
| |
| 作者单位: | 1.江苏南京地质工程勘察院,南京 210041; 2.东南大学能源与环境学院,能源转换及其过程测控教育部重点实验室,南京 210096 |
| |
| 基金项目: | 江苏省环境工程重点实验室科研开放基金 |
| |
| 摘 要: | 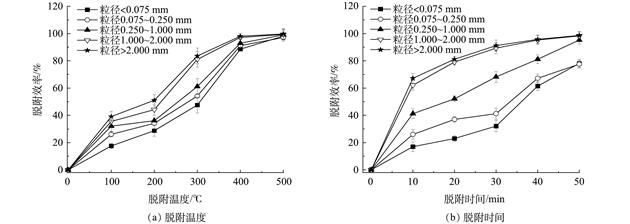
针对石油烃污染土壤成分复杂、污染严重、修复难度高的问题,采用适用性广、效率高且去除彻底的异位热脱附技术修复石油烃污染土壤。利用碳数分段法及室内模拟实验,探究在热脱附过程中的土壤粒径、含水率和有机质对石油烃及各组分热解吸效率的影响;另外,还采用响应面法对各影响因素进行了优化,以获得异位热脱附修复石油烃污染土壤的最优工艺参数。结果表明,当污染土壤粒径高于1 mm时,石油烃脱附效率均可达90%以上,且粒径越大土壤颗粒中石油烃去除率越高。其中,润滑油段(ORO, C28~C40)组分的脱附效率随粒径变化最为明显。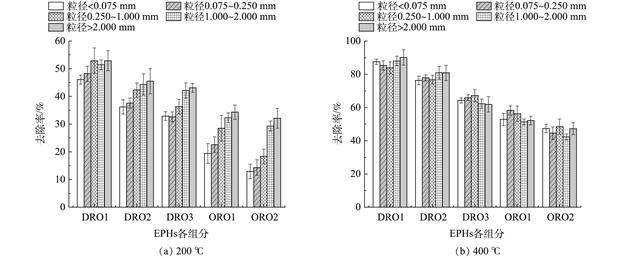
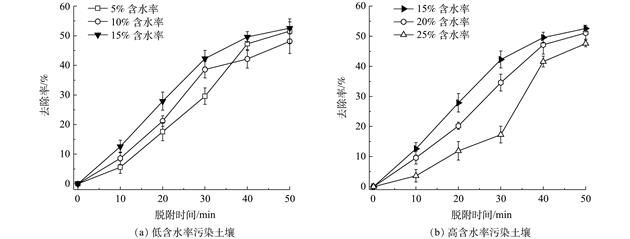
当土壤含水率为15%、脱附时间为50 min时,石油烃脱附效率最大为52.63%。另外,土壤中有机质含量越低,越利于石油烃的脱除,且高温(400~500 ℃)条件下可基本消除土壤中高含量有机质(3.82%)对石油烃脱除的阻碍作用。响应面优化实验得到的最佳工艺参数条件为,粒径2 mm、有机质含量1.44%、含水率为17.68%,在此条件下的石油烃脱附去除效率可达65.32%。该研究结果可为热脱附技术在石油烃污染场地的实际应用提供参考。
|
| 关 键 词: | 碳数分段法 石油烃污染土壤 异位热脱附技术 响应面优化 |
| 收稿时间: | 2020-11-26 |
| 本文献已被 万方数据 等数据库收录! |
| 点击此处可从《环境工程学报》浏览原始摘要信息 |
|
点击此处可从《环境工程学报》下载免费的PDF全文 |
|



