|
|||||
|
|
| 基于微生物生物完整性指数的北京市城市河道生态系统健康评价 | |
| 引用本文: | 董婧,卢少奇,伍娟丽,等.基于微生物生物完整性指数的北京市城市河道生态系统健康评价[J].环境工程技术学报,2022,12(5):1411-1419 doi: 10.12153/j.issn.1674-991X.20210368 |
| 作者姓名: | 董婧 卢少奇 伍娟丽 王子康 王恒嘉 徐菲 |
| 作者单位: | 1.北京市环境保护科学研究院;;2.国家城市环境污染控制工程技术研究中心;;3.首都师范大学 |
| 基金项目: | 北京市环境保护科学研究院基金项目(Y2010-010);北京市环境保护科学研究院纵向结余项目(JZ2020-005,JZ2021-008) |
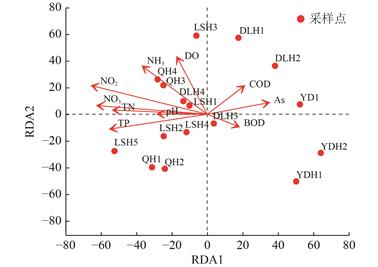
| 摘 要: | 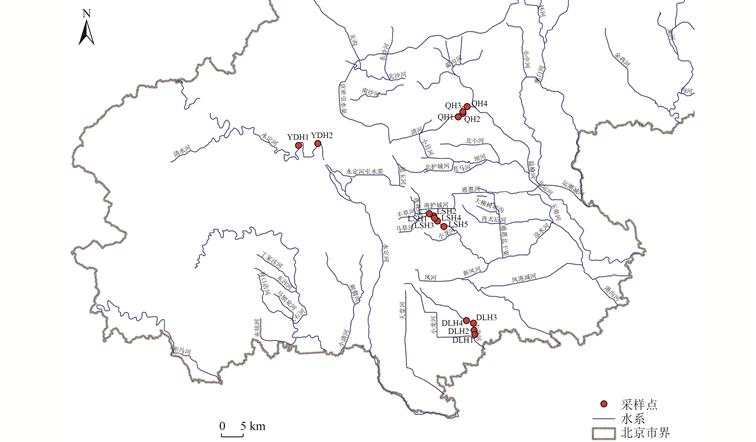 生物完整性指数(IBI)是河道生态系统健康评价的重要且被广泛应用的指标,然而,基于水体中分解者微生物群落构建IBI评价标准的研究较少。针对北京市城市河道生态系统健康状况开展评价,探索微生物生物完整性指数(M-IBI)评价流程与标准构建方法。基于沉积物中微生物Illumina高通量测序信息,筛选出关键环境因子(水质指标TN、TP、NH3-N、NO3-N和NO2-N)确定候选生物指标,根据判别能力分析结果,确定Shannon指数、拟杆菌门(Bacteroidota)相对丰度、绿弯菌门(Chloroflexi)相对丰度、蓝藻门(Cyanobacteria)相对丰度、CODCr耐受属相对丰度和NH3-N清洁属相对丰度6个指标,提出了指标标准化公式和健康评价标准。 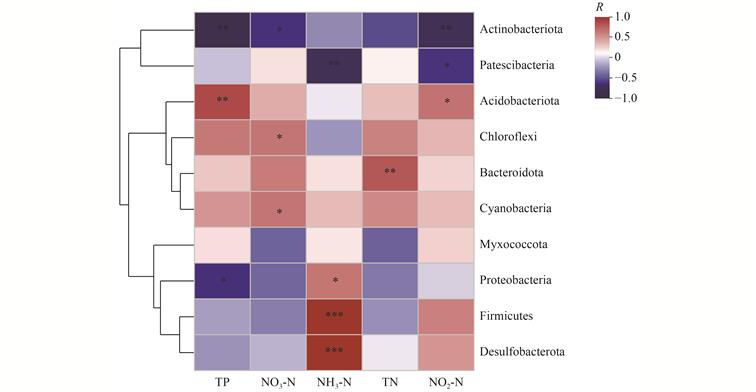 |
| 关 键 词: | 微生物生物完整性指数(M-IBI) 生态系统 城市河道 健康评价 微生物群落结构 |
| 收稿时间: | 2021-08-02 |
| 点击此处可从《环境工程技术学报》浏览原始摘要信息 | |
| 点击此处可从《环境工程技术学报》下载免费的PDF全文 | |