| MnFeCu-LDHs活化PMS降解氯四环素的效能及机制 |
| |
| 引用本文: | 朱建宇, 党清平, 杨帆, 李军, 吴嘉平, 田亚军. MnFeCu-LDHs活化PMS降解氯四环素的效能及机制[J]. 环境工程学报, 2022, 16(12): 3895-3905. doi: 10.12030/j.cjee.202209108 |
| |
| 作者姓名: | 朱建宇 党清平 杨帆 李军 吴嘉平 田亚军 |
| |
| 作者单位: | 1.浙江大学海洋学院,舟山 316021; 2.中国市政工程华北设计研究总院有限公司,天津 300074; 3.浙江工业大学环境学院,杭州 310014 |
| |
| 基金项目: | 浙江省自然科学基金资助项目(LQ22E080027);国家自然科学基金资助项目(42107411) |
| |
| 摘 要: | 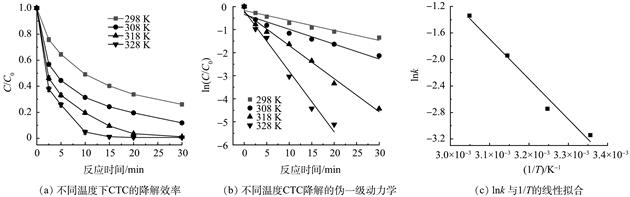
针对污水处理厂尾水中抗生素等生物难降解有机物频繁检出的问题,采用相对绿色、低毒性的过渡金属元素制备了锰铁铜类水滑石(MnFeCu-LDHs),并将其用于活化过一硫酸盐(PMS)降解氯四环素(CTC)。探究了初始pH、反应温度、催化剂和PMS投量对CTC降解效能的影响规律,通过化学捕获和淬灭实验确定了活性氧物种(ROS)的种类与贡献,并对反应前后的催化剂进行理化性质表征且考察了催化剂稳定性。结果表明,在初始pH为7、反应温度为298 K、催化剂及PMS投加量均为0.2 g·L−1条件下,反应5 min后CTC去除率达到80.88%,30 min去除率达到91.18%,同时,随着初始pH和温度的提高,CTC的降解效果得到明显增强;ROS淬灭实验和EPR捕获实验结果证实了在该体系中,·OH、SO4·−、1O2均参与了CTC的降解,贡献度最高的是1O2,其次为·OH和SO4·−;基于反应前后XPS光谱对比分析,发现MnFeCu-LDHs活化PMS过程稳定性较好,此外该催化剂在重复使用5次后,CTC的30 min去除率仍达到73.61%。因此,本研究可为SR-AOPs应用于控制水环境抗生素类污染提供新思路。
|
| 关 键 词: | MnFeCu-LDHs 过一硫酸盐 高级氧化技术 氯四环素 氧化降解 |
| 收稿时间: | 2022-09-19 |
|
| 点击此处可从《环境工程学报》浏览原始摘要信息 |
|
点击此处可从《环境工程学报》下载全文 |
|

