-
城市污水排放是地表水最重要的人为氮源污染之一[1]。近年来,为了更好地调控受纳水体的富营养化风险,污水处理厂的总氮排放标准越来越严格,包括美国、欧洲和中国的部分地区甚至要求出水达到超低总氮排放限值 (5~10 mg·L−1) [2]。除了溶解性无机氮 (即氨氮、硝态氮和亚硝态氮) ,溶解性有机氮 (DON) 作为污水处理厂重要的出水氮组分越来越受到关注。特别是在无机氮脱除技术不断提标以及总氮排放限值愈发严苛的背景下,DON在污水总氮中的占比越来越高 (>65%) [3]。以往的研究表明,DON是一种潜在的生物可利用氮源,相当一部分DON可以很容易的被藻类和细菌利用[4]。EAM等[5]研究发现DON表现出比无机氮更强的刺激浮游植物生长的能力。目前常使用可以支持藻类生长的DON占总DON的比例来代表DON的生物有效性,用以表征污水DON的富营养化潜能[6-7]。活性污泥法是污水处理厂中最广泛应用的技术,其中好氧活性污泥法比厌氧和缺氧活性污泥法更容易导致较高的出水DON浓度[8]。因此,探讨调控好氧活性污泥法中DON的技术方法,尤其是从生物有效性的角度,对于有效保护受纳水体水质具有重要的意义。
投加外源金属二价阳离子 (如Mg2+、Ca2+、Fe2+、Mn2+) 可以通过影响微生物的表面电荷分布,酶活性等方式影响活性污泥系统的水处理能力影响出水水质[9]。例如,ZHANG等[10]研究发现投加镁离子 (Mg2+) 浓度低于1.1 mmol·L−1时,好氧活性污泥硝化活性显著提高,但在镁离子浓度达到3 mmol·L−1时硝化活性受到抑制。SINDHU等[11]在厌氧氨氧化系统中发现亚铁离子 (Fe2+) 添加对污泥胞外聚合物产量和脱氮效果有很大影响,当添加1 mmol·L−1 Fe2+时,氨氮和硝态氮去除率可以分别达到94.33%和94.84%。樊艳丽等[12]发现钙离子 (Ca2+) 会影响活性污泥系统的总氮 (TN) 去除率。所以投加适量外源金属离子常被用作强化好氧活性污泥处理性能的方法。其中,Ca2+被发现可以能够影响污泥的代谢产物,如胞外聚合物 (EPS) 和微生物溶解性产物 (SMP) 。这些代谢产物主要是蛋白质和多糖,与污水中的DON直接相关。ZHANG等[13]发现投加168.5 mg·L−1的钙离子能够有效减少微生物絮体中松散结合的EPS和上清液中SMP。ARABI和NAKHLA[14]也在140 mg·L−1的钙离子投加量下发现了污泥上清液中SMP的降低。综上表明,向活性污泥系统适量投加钙离子具有调控出水DON的潜力。然而,目前对于钙离子对好氧活性污泥DON的影响及内在微生物作用机理仍不明确。
本研究旨在探究外源钙离子对好氧活性污泥DON及其生物有效性的影响,并基于超高分辨率的傅里叶变换离子回旋共振质谱 (FTICR-MS) 分析DON的分子特征,解释其生物有效性变化的原因。最后,通过分析微生物的生理变化特征及群落结构尝试从微生物角度阐释钙离子影响好氧活性污泥DON的内在机理。本研究的结果将为污水处理厂中好氧活性污泥法的出水DON控制提供实践指导,以更好地调控出水氮的富营养化潜能,降低污水排放对于水环境的负面影响。
-
本研究以钙离子浓度为外源物质,设置钙离子浓度水平为0.01、0.05、0.1以及1 mmol·L−1为实验组、钙离子浓度水平为0 mmol·L−1为对照组,探究外源投加钙离子对好氧活性污泥DON去除效果的影响。采用实际废水 (市政污水厂一级处理出水) 作为进水,本研究中进水的COD是126.73~172.38 mg·L−1、TN浓度是29.74~44.07 mg·L−1、TP浓度是2.51~3.27 mg·L−1、DON浓度是7.94~12.32 mg·L−1。当地的市政污水厂一级出水的DON浓度也基本在5.94~13.92 mg·L−1范围内,这表明本研究的进水有机氮水平具有代表性。本研究通过外加CaCl2调节水中钙离子浓度,每个浓度水平设置2个平行,搭建好氧活性污泥反应器。监测指标为反应器出水中的基本水质参数 (COD、无机氮各项指标、DON) 、DON分子组成以及微生物特性。反应器运行3个SRT后各项基本水质指标趋于稳定。
-
化学需氧量 (COD) 采用快速密闭催化消解法测定[15]。DON的浓度表示为总溶解氮 (TDN) 减去所有的无机氮,包括氨氮 (NH4+-N) 、硝态氮 (NO3−-N) 和亚硝态氮 (NO2−-N) 。TDN测定通过过硫酸盐消化法将样品氧化成NO3−-N,然后采用离子色谱法定量NO3−-N的浓度[16]。NH4+-N采用水杨酸法进行测定。NO3−-N和NO2−-N使用离子色谱法 (Dionex ICS-1100,美国赛默飞世尔科技有限公司) 进行测定[16]。
-
首先采用14 d藻类生物培养实验测定可被藻类利用的DON (ABDON) 。选用中国科学院淡水藻种库 (FACHB-collection) 中被广泛用于水体富营养化表征的羊角月牙藻 (Selenastrum capricornutum) 作为测试藻种。将1.5 mL的藻类接种液和1 mL污水厂的混合培养菌添加到250 mL锥形瓶中的100 mL污水DON样品中。将锥形瓶置于22~25 ℃的温控摇床中培养,提供12 h∶12 h的光照:黑暗条件以模拟藻类生长真实环境条件[6]。用去离子水作为对照组。生物有效性的计算公式如式(1)和式(2)[17]。
式中:ABDON代表可被藻类利用的DON浓度,mg·L−1;DONi和DONf分别代表污水样品培养前后的DON浓度,mg·L−1;DONbi和DONbf分别代表去离子水样品培养前后的DON浓度,mg·L−1。
-
所有的污水样品均采用PPL固相萃取柱来富集DON。在萃取之前,首先使用HPLC级的甲醇和盐酸溶液 (pH=2) 活化萃取柱。然后,将酸化后的水样 (pH=2,由盐酸调整) 以2 mg·min−1的流速通过PPL柱,随后使用pH=2的盐酸溶液冲洗柱子,并用氮气吹扫干燥[18]。最后,使用10mL甲醇对PPL柱进行洗脱[18]。洗脱液用甲醇稀释后以供进一步FTICR-MS分析。本研究采用15 T FTICR-MS (Bruker,德国布鲁克光谱仪器有限公司) ,配备负离子模式的电喷雾电离 (ESI) 源,分析样品中DON的分子组成。用注射泵将样品以180 μL·h−1的流速注入ESI源。使用Bruker数据分析软件 (v.4.1) 对原始峰进行识别,筛选出质量在200~700 m/z范围内信噪比S/N>6的峰进行分子式计算[19]。分子式根据以下元素进行分配:碳 (C,2~50) 、氧 (O,0~30) 、氢 (H,2~120) 、氮 (N,0~6) 、磷 (P,0~2) 和硫 (S,0~2) 。原子数量之间必须满足2≤H≤(2C+2)、O≤(C+2)、O/C<1.2、0.333≤H/C≤2.25、N/C<0.5、S/C<0.2、P/C<0.1、(S+P)/C<0.2、P<O/3,用以排除极不可能在DON中出现的分子式。本研究采用不饱和等效双键数 (DBE) 和碳的平均氧化态 (NOSC) 来表征DON的分子特征,计算公式如式(3)和式(4)[20]。
-
本研究选择三磷酸腺苷 (ATP) 、琥珀酸脱氢酶 (SDH) 、脱氢酶 (DHA) 、比耗氧速率 (SOUR) 探究不同外源钙离子浓度下好氧活性污泥的微生物活性[21]。ATP浓度使用 BacTiter-Glo™ 微生物细胞活性检测试剂盒进行测定[22]。SDH活性采用琥珀酸脱氢酶活性比色测定试剂盒测定,SDH的最终浓度通过BCA蛋白质测定试剂盒测量的蛋白质浓度进行标准化[21]。DHA活性通过测量 2,3,5-三苯基氯化四氮唑 (TTC) 还原成三苯基甲臜 (TPF) 的量来测定[23]。SOUR通过使用溶解氧测量仪测定一定时间内好氧活性污泥的耗氧量进行计算。另外,本研究还通过测定微生物细胞膜上磷脂脂肪酸 (PLFA) 的变化知识微生物活动的变化。PLFA分析依据NIU等[24]提供的方法进行,包括分离、洗脱、萃取和皂化甲基化。使用固相萃取柱分离得到磷脂,皂化甲基化后的脂肪酸甲酯采用气相色谱仪 (Agilent 7890,美国安捷伦科技有限公司) 测定,最后使用MIDI Sherlock微生物鉴定系统对结果进行分析。
-
从好氧污泥反应器中各收集3个平行的污泥样本,使用 FastDNA土壤试剂盒对s6个反应器中的污泥进行 DNA 提取。然后,DNA提取物被送往上海生工生物工程技术服务有限公司进行16S rRNA基因PCR扩增,PCR产物纯化和随后的Illumina MiSeq测序[25]。最后,使用Mothur软件包 (v.1.35.1) 进行数据分析[26]。
-
采用SPSS统计软件进行显著性差异分析 (单因素方差分析,ANOVA) ,当p值为<0.05认为是差异是显著的。冗余分析 (RDA) 使用CANOCO 4.5软件进行,用以探讨DON浓度及特征与微生物之间的相关关系[25]。
-
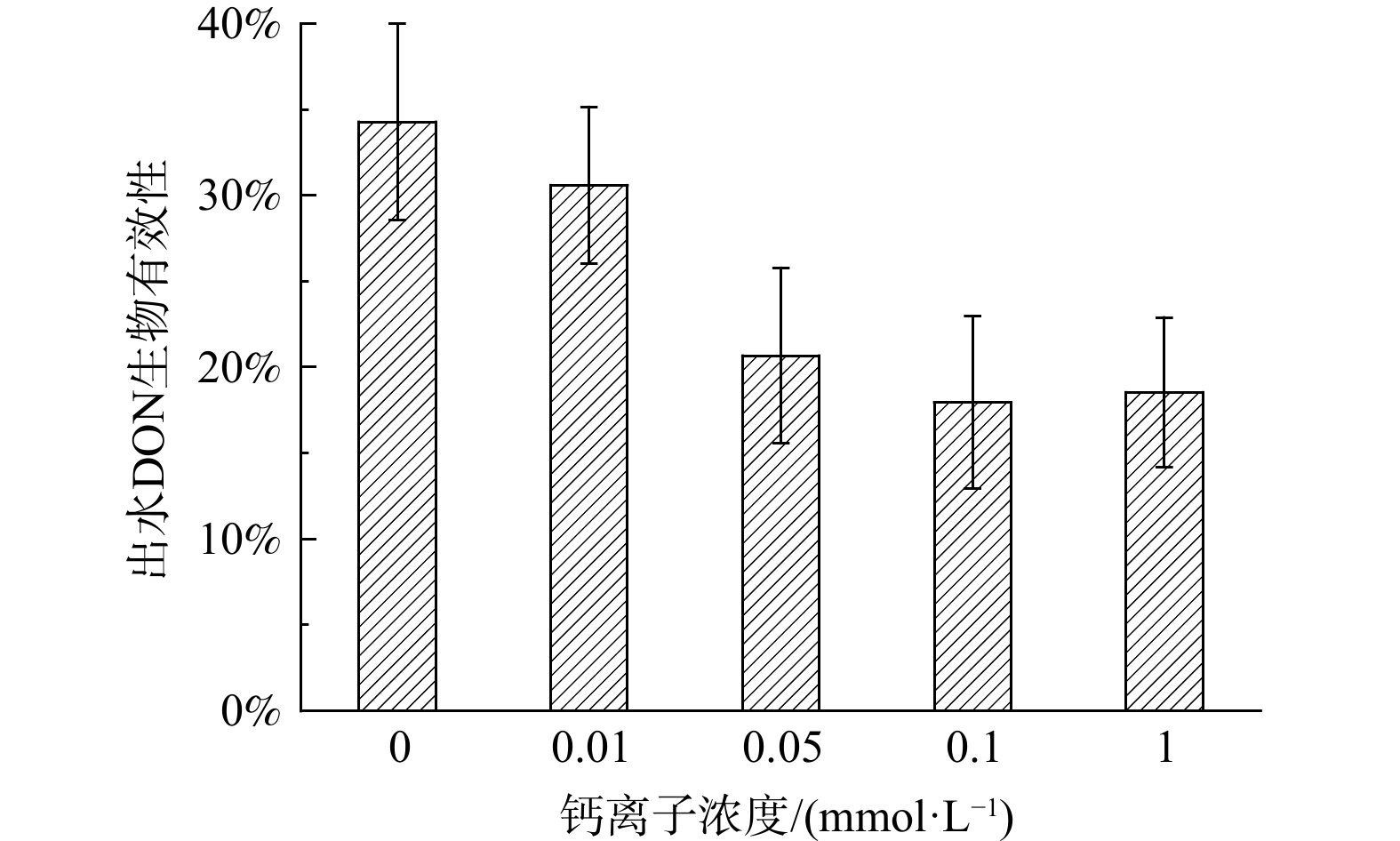
通过对比5组反应器出水DON浓度,可探究外加钙离子对于好氧活性污泥反应器DON去除效率的影响。由图1可知,随着外加钙离子浓度的增加,反应器出水DON的浓度表现出先降低后增加的趋势。其中,空白组出水DON浓度为(2.19±0.18) mg·L−1 (0 mmol·L−1,Ca2+) ,当外加钙离子浓度为0.01~1 mmol·L−1,出水DON浓度为1.46~2.13 mg·L−1。增效阈值的现象存在于外加钙离子对于好氧活性污泥去除DON的作用中。对于本研究中设定实验条件,外加钙离子对于提高好氧活性污泥反应器DON去除效果的阈值为0.1 mmol·L−1,此时出水DON浓度为1.46±0.12 mg·L−1, 出水DON浓度相比于空白组降低了33.3%。当外加钙离子浓度低于0.1 mmol·L−1,随着钙离子浓度增加,出水DON浓度降低;当外加钙离子浓度高于0.1 mmol·L−1,随着钙离子浓度增加,出水DON浓度升高。同时,对比其他基本出水水质指标可知,外加钙离子在其中的增效作用阈值同样为0.1 mmol·L−1。TANG等[27]研究在微藻-细菌共生系统中也观察到相似的结果,较低的钙离子 (Ca2+) 负荷 (即0.1 mmol·L−1) 可以促进中COD和营养物质的去除。因此,对于基本水质以及出水DON浓度而言,0.1 mmol·L−1的外加钙离子浓度是提高好氧活性污泥反应器处理性能的最佳取值。
如图2所示,出水生物DON的生物有效性与DON浓度随外加钙离子浓度的增加先降低后增加,也呈现出相似的阈值现象。空白组出水DON有效性为34.29%±0.06% (0 mmol·L−1,Ca2+) 。当外加钙离子浓度为从0.01 mmol·L−1增加到0.1 mmol·L−1时,好氧活性污泥出水的DON生物有效性从30.60%±0.05%降低至17.97%±0.05%;当外加钙离子浓度提高到0.1 mmol·L−1时,DON的生物有效性又提高至18.54%±0.04%。生物有效性DON基于藻类生长表征DON的富营养化潜能,能够更加直接地呈现外加钙离子对于好氧活性污泥反应器出水对于自然水体水质的影响[28]。因此上述结果表明,对于本研究的实验条件,基于DON的生物有效性,0.1 mmol·L−1仍是外源钙离子对于降低好氧活性污泥反应器DON生物有效性、管控DON富营养化潜能排放的最佳阈值浓度,此时DON的生物有效性相比于空白组降低了47.6%。值得讨论的是,城市污水处理厂中的一般本底钙离子浓度为30~60 mg·L−1 (0.75~1.5 mmol·L−1) [29]。本研究中0.1 mmol·L−1的钙离子最佳投加浓度阈值对于体系造成的改变并不算是极少的。因此,在考虑了实际污水处理厂的本底钙离子浓度水平后,本研究中所应用的外源钙离子浓度仍然具有能够显著影响好氧活性污泥系统的潜力。
-
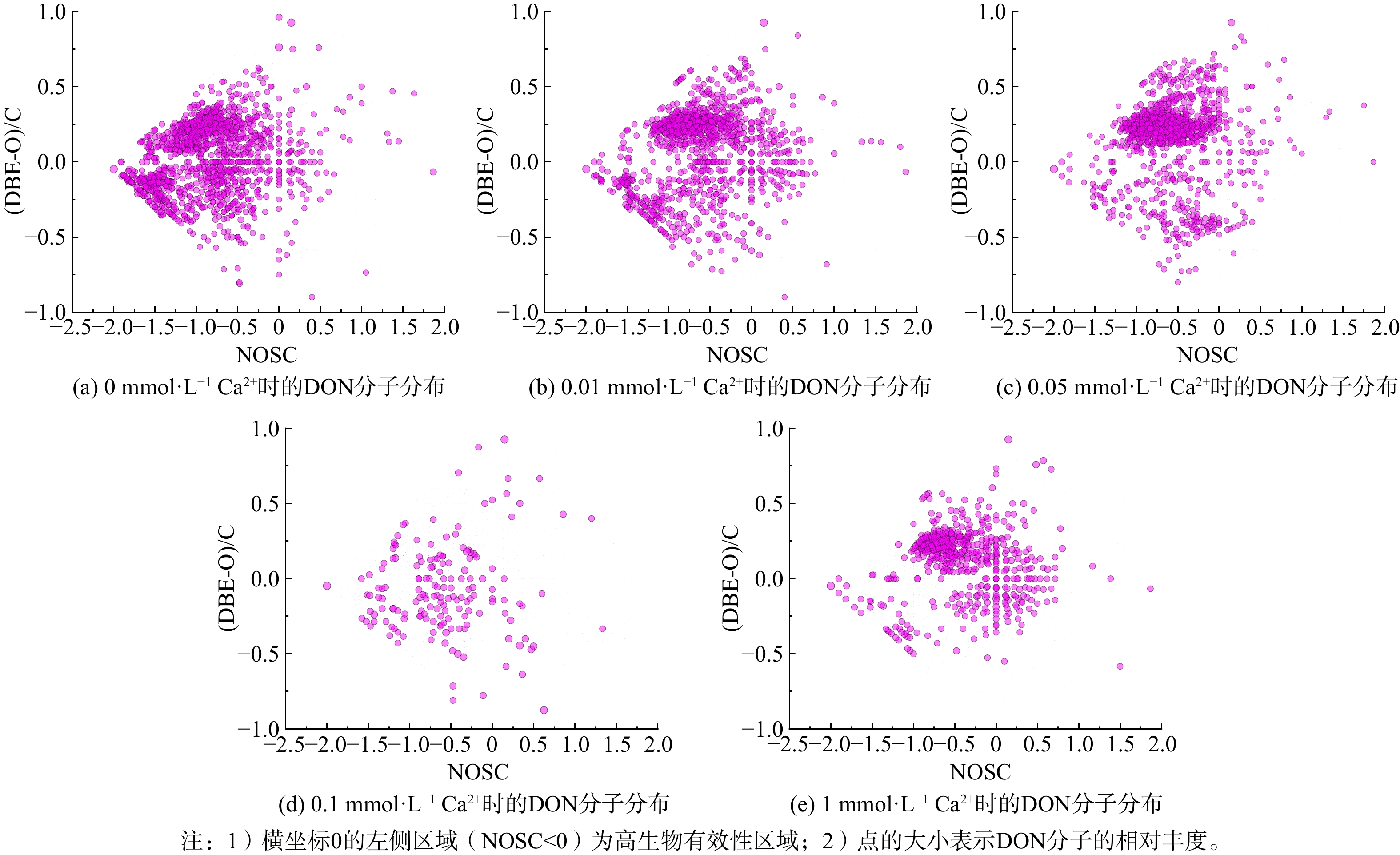
DON的生物有效性与它的分子化学性质密切相关[30]。为了从分子层面解析外加钙离子对好氧活性污泥反应器出水DON生物有效性的影响,采用FTICR-MS进一步分析DON的分子组成特征 (图3) 。NOSC通常用来反应分子的氧化还原状态,而氧化还原状态已经被证实与微生物活动密切相关[31]。已有研究指出,低平均碳氧化态的DON分子 (NOSC<0) 主要包括氨基酸、脂质、蛋白质和不饱和烃[32],这些分子更容易被藻类微生物降解利用[33],因此是高生物有效性的组分。ZHANG等[18]在研究中发现NOSC与难降解的芳香化合物 (用SUVA254指示) 和类腐殖酸呈现负相关,这也侧面证实了低NOSC的分子可能更加容易生物降解。因此,本研究选择NOSC<0的分子代表高生物有效性的分子。
如图3所示,不同外加钙离子浓度下,好氧活性污泥的DON分子均主要分布在NOSC<0的高生物有效性区域。这与HUO等[8]在A/A/O工艺中关于好氧活性污泥产生更多容易降解的微生物代谢DON的推测一致。韩成龙等[15]也发现好氧段出水中易生物降解的DON占比更高。此外,好氧活性污泥反应器出水中NOSC<0的DON分子数量随外加钙离子浓度变化的趋势与由藻类直接测定的生物有效性变化相同,呈现先减少后增加的趋势,且阈值同样出现在0.1 mmol·L−1 (图3) 。空白组出水DON中位于高生物有效性区域的分子最多 (0 mmol·L−1,Ca2+) 。当外加钙离子浓度在0~0.1 mmol·L−1范围内逐渐增加时,NOSC<0的DON分子逐渐减少;当外加钙离子浓度大于0.1 mmol·L−1时,NOSC<0的DON分子增加。因此可以合理推断外加钙离子通过影响好氧活性污泥反应器中氧化程度较低的分子 (NOSC<0) 影响DON的生物有效性,从而调控出水DON的富营养化潜能。
-
在好氧活性污泥系统中,DON的去除依赖活性污泥微生物的降解与转化作用。并且,已有研究探明,适量浓度的外加钙离子可以增加活性污泥系统的TN去除能力[12]。微生物在好氧活性污泥脱氮的过程中扮演着关键角色,介导了外加钙离子对于DON浓度的影响。出水DON是出水TN的重要组成部分,因此可从微生物学角度进行阐述外加钙离子调控DON去除过程的机理。据已有研究报道,外加钙离子可通过改变微生物活性、驯化相应的微生物、促进微生物群落的演替,从而改变系统中微生物的水处理能力,进而改变出水水质[34]。其中,微生物活性涉及微生物酶活、微生物活性物质,或其他可指代微生物活性的相关指标,如ATP、DHA酶活、SDH酶活、SOUR等[21, 23]。本研究通过分析不同外加钙离子浓度下微生物活性的变化以及微生物群落结构的演替,解析外加钙离子调控DON去除过程的内在机理。
微生物ATP测试结果如图4(a)所示,空白组中,ATP浓度为(10.32±0.93) μg· (g MLSS) −1;实验组中,随着外加钙离子浓度逐渐升高,ATP浓度出现先增后减趋势,ATP浓度分别为(12.35±0.55) μg· (g MLSS) −1 (0.01 mmol·L−1 Ca2+) 、(17.02±0.79) μg· (g MLSS) −1 (0.05 mmol·L−1 Ca2+) 、(16.62±0.21) μg· (g MLSS) −1 (0.1 mmol·L−1 Ca2+)、(8.97±0.92) μg· (g MLSS) −1 (1 mmol·L−1 Ca2+) 。对比空白组与实验组结果可知,外加钙离子对于ATP的作用同样具有阈值效应。ATP是为微生物生长代谢过程提供能量的物质,一定程度上ATP浓度的升高可表明微生物生长代谢活动的增加,因此活性污泥中ATP的浓度可指示微生物活性的高低[35]。升高的ATP表明外加钙离子可在一定程度上提高微生物的代谢活性。
SDH酶、DHA酶与ATP相似,是表征微生物代谢活性过程中常见的指示物质。如图4(b)所示,SDH酶浓度为(16.89±0.67) U· (mg protein)−1 (0 mmol·L−1,Ca2+)、(22.01±1.08) U· (mg protein)−1 (0.01 mmol·L−1,Ca2+)、(24.49±0.81) U· (mg protein)−1 (0.05 mmol·L−1,Ca2+)、(26.95±2.11) U· (mg protein)−1 (0.1 mmol·L−1,Ca2+) 、(14.42±0.64) U· (mg protein)−1 (1 mmol·L−1,Ca2+) ,结果表明外源钙离子添加浓度为0.05~0.1 mmol·L−1时,SDH酶活较高、微生物代谢能力较强。该结果显示的钙离子浓度的阈值 (0.1 mmol·L−1) 与本研究中好氧活性污泥的DON浓度和DON生物有效性所呈现的阈值一致。SDH酶是三羧酸循环中的关键酶,可作为评价三羧酸循环的指标[36]。已有研究表明生物有效性的DON包括氨基酸、脂质等分子,而三羧酸循环作为糖类、脂类和氨基酸的最终代谢通路[37],能够影响微生物对这部分DON的去除。因此SDH酶活变化一定程度上反映了出水DON生物有效性变化的原因。另外注意到,SDH酶活性与ATP浓度随钙离子浓度变化的趋势类似,但外加钙离子对于SDH酶活的阈值为0.1 mmol·L−1,而对于ATP的阈值为0.05 mmol·L−1,二者略有区别。这种阈值的差别可能与两种酶在微生物代谢过程中的功能差异相关。另一方面,微生物降解污染物时,有机物在微生物细胞中的氧化作用一般通过脱氢作用获得能量,DHA酶是微生物代谢过程发挥作用的重要生物酶[38]。如图4(d)所示,DHA酶在外加钙离子浓度为0.05 mmol·L−1时,具有最大活性,为(7.17±0.22) mg TF·(g MLSS) −1。总体而言,随着外加钙离子浓度升高,3种生物酶活性变化趋势相近,均为活性先增加至某一阈值后降低。这表明,外加钙离子可能通过影响与微生物代谢活动有关的酶活性影响到DON,尤其是生物有效性DON的去除。
在现有研究中,常使用SOUR表示单位时间内单位质量活性污泥消耗氧气的体积。在好氧活性污泥系统中,好氧微生物氧化有机物产能代谢的过程主要是以氧气作为最终电子受体。因此相应地,SOUR数值的大小也可直接反映好氧活性污泥系统中微生物活动的变化[39]。如图4(c)所示,随着外加钙离子浓度由0.01 mmol·L−1增加至0.1 mmol·L−1,SOUR数值逐渐上升;当外加钙离子浓度增加至1 mmol·L−1,SOUR数值虽略有下降,但与钙离子浓度为0.1 mmol·L−1时无统计学意义的差别 (p>0.05,ANOVA) 。SOUR与DON浓度和生物有效性相近的阈值现象也进一步证明了外加钙离子导致的DON浓度及DON生物有效性的变化与微生物代谢有机物的活性密切相关。综上所述,一定浓度的外加钙离子能够提高好氧活性污泥中微生物的代谢活性,通过增强微生物对有机物的氧化代谢提高有机物的去除率,从而降低了好氧出水的DON。张兰河等[40]也在研究中发现适量外源钙离子的投加提高了活性污泥体系中DHA酶活性和SOUR。虽然外源钙离子在提高微生物代谢活性的同时增加了EPS的合成,但带正电的钙离子可以与EPS表面带负电的官能团形成架桥,二者的络合不仅提高了污泥的絮凝沉降性能,也使得松散结合型EPS的比例 (LB-EPS/EPS) 降低[40-41]。由于LB-EPS与SMP的形成密切关联[13],且SMP中由微生物产生的蛋白质等物质又是生物有效性DON的重要组成部分,因此钙离子与EPS的络合作用也一定程度上支持了本研究中适量外源钙离子促进出水DON影响浓度及生物有效性降低的发现。
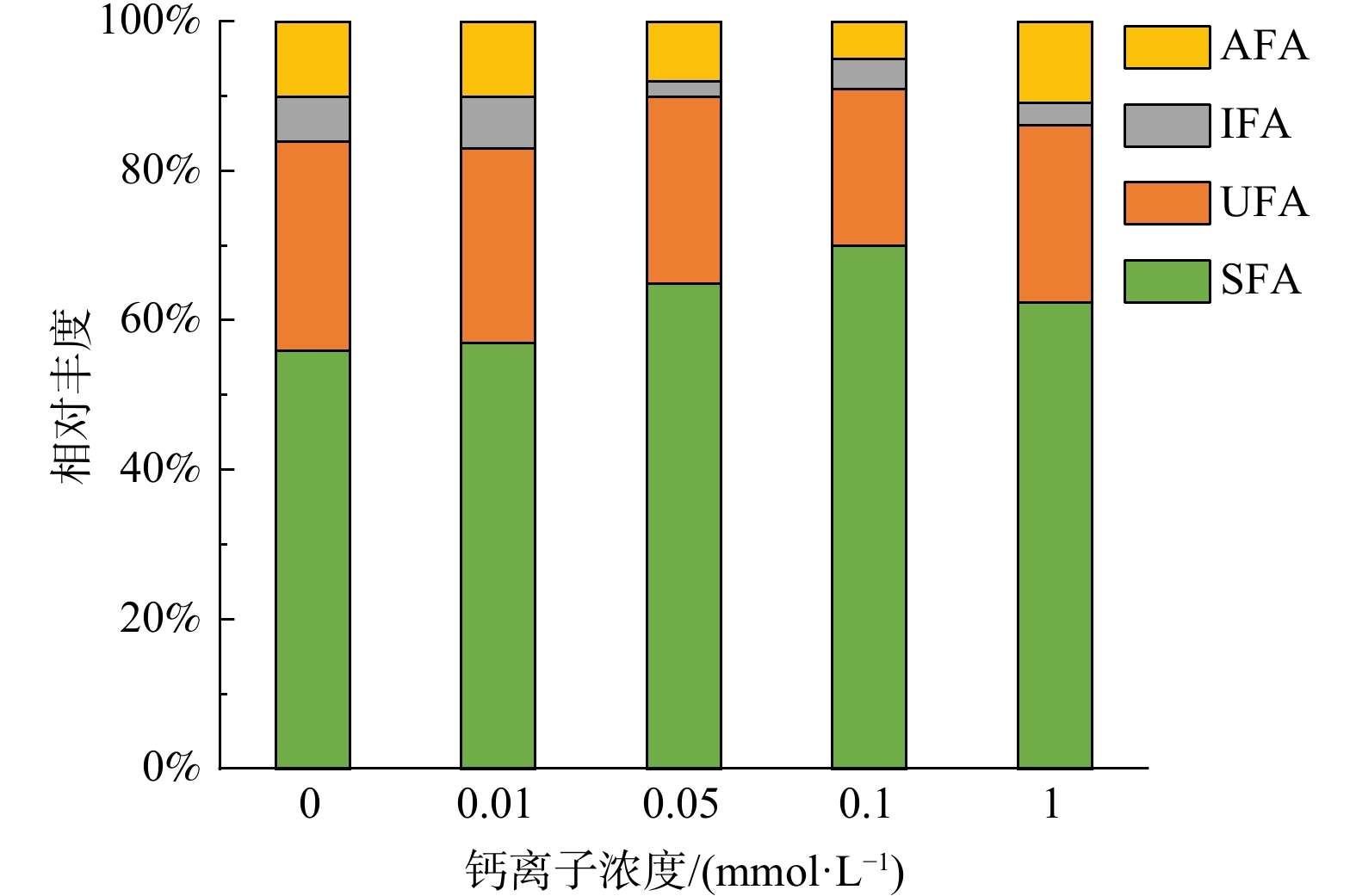
除了生物酶活,微生物细胞膜的组成也可以作为辅助指标指示微生物活性的变化。PLFA是微生物细胞膜磷脂双分子层的主要组成部分,多存在于活性微生物中,微生物死亡后PLFA会被迅速降解。并且PLFA可进一步分类为饱和脂肪酸 (SFA) 、不饱和脂肪酸 (UFA) 、异构脂肪酸 (IFA) 和反式异构脂肪酸 (AFA) [42]。图5展示了不同外加钙离子浓度对微生物细胞膜的影响。结果表明,5组反应器中,饱和脂肪酸 (SFA) 在细胞膜组成中相对丰度由大到小为:外加钙离子浓度为0.1 mmol·L−1时 (69.91%) >外加钙离子浓度为0.05 mmol·L−1时 (64.79%) >外加钙离子浓度为1 mmol·L−1时 (62.35%) >外加钙离子浓度为0.01 mmol·L−1时 (56.40%) >空白组(55.37%)。不饱和脂肪酸 (UFA) 在细胞膜组成中相对丰度由大到小为:空白组 (28.79%) >外加钙离子浓度为0.01 mmol·L−1时 (26.58%) >外加钙离子浓度为0.05 mmol·L−1 (24.95%) >外加钙离子浓度为1 mmol·L−1时 (22.79%) >外加钙离子浓度为0.1 mmol·L−1时 (20.69%) 。细胞膜组成中的饱和脂肪酸与不饱和脂肪酸是评价细胞膜流动性的重要指标。已有研究报道,微生物在环境影响下会自发改变细胞膜PLFA组成,通过调节饱和脂肪酸/不饱和脂肪酸在细胞膜中的占比调节细胞膜流动性[42]。基于不同外加钙离子浓度下好氧活性污泥反应器中DON浓度的变化结果,外加钙离子浓度为0.1 mmol·L−1为提高好氧活性污泥反应器去除DON效率的最佳取值。当外加钙离子浓度为0.1 mmol·L−1时细胞膜饱和脂肪酸占比最高 (64.79%),不饱和脂肪酸 (20.69%) 和反式异构脂肪酸占比最低 (5.12%) 。在微生物细胞膜组成中,反式异构脂肪酸具有与不饱和脂肪酸相同的作用,通过破坏磷脂酰基链的紧密堆积从而改变细胞膜流动性[43-44]。因此,反式异构脂肪酸在细胞膜中相对丰度增加,会提高细胞膜流动性。据报道,细胞膜的流动性极大地影响了微生物胞内许多与结构或功能无关的化合物的运输和排出,这可能对微生物代谢的DON产物的释放产生重要影响[45-46]。MA等[45]研究表明细胞流动性越低,出水蛋白质含量越低。在本研究中,出水DON浓度和生物有效性最低时 (外加钙离子浓度为0.1 mmol·L−1) ,细胞膜组成的分析结果都表明了细胞膜组成转变为流动性更低的状态,这可能阻滞了微生物代谢产生的DON的排放,从而使得在该浓度下能达到最佳的出水DON排放浓度和生物有效性。
微生物群落结构是影响好氧活性污泥系统水处理效果的重要因素之一。因此,对比5组反应器在不同外加钙离子浓度下微生物群落结构的变化,可进一步解析最优钙离子投加条件下 (外加钙离子浓度为0.1 mmol·L−1) 促使DON去除效率最高的原因。图6展示了5组反应器在稳定期微生物群落在属水平的分布。除尚无对应分类名录的菌种外,在属水平上的主要微生物菌种 (按照5组反应器中相对丰度值由大到小) 为Saccharibacteria_genera_incertae_sedis、Propionicicella、Luteolibacter、Ferruginibacter、Defluviimonas、Dechloromonas、Rhodoferax、Blastocatella、Sphingorhabdus、Ferribacterium等。其中值得注意的是,Luteolibacter为微生物群落中发挥降解有机物作用的好氧菌[47],是指示微生物群落对有机物去除能力的重要菌种。对比不同外加钙离子浓度下Luteolibacter菌的相对丰度变化可知,当外加钙离子浓度由0.01 mmol·L−1增加至0.1 mmol·L−1时,Luteolibacter菌相对丰度由2.07%富集至7.44%;当外加钙离子浓度由0.1 mmol·L−1增加至1 mmol·L−1时,Luteolibacter菌相对丰度下降至3.56%。这说明Luteolibacter菌在钙离子调控的环境下,其存活状态同样具有生存阈值,在一定范围内,外加钙离子可通过富集时Luteolibacter菌强化系统对有机物去除的能力,从而提高DON去除率。一定程度而言,在外加0.1 mmol·L−1钙离子调控好氧活性污泥系统的DON去除过程中,Luteolibacter菌扮演着不可忽视的作用。因此,外源钙离子可能通过调整微生物群落结构,尤其是提高降解有机物的好氧菌的相对丰度,强化对于好氧活性污泥反应器中DON的去除。
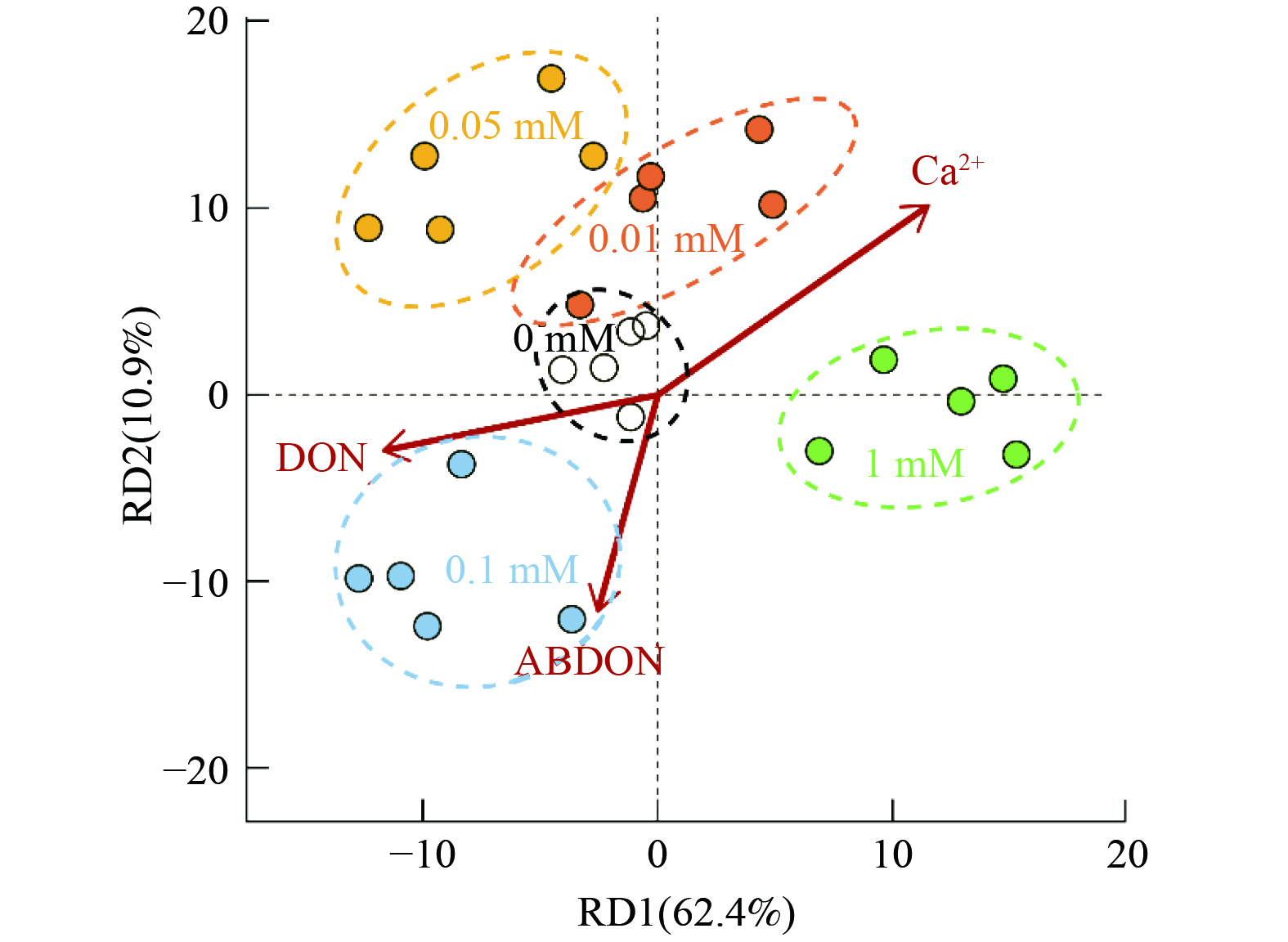
进一步地,为揭示在外源钙离子调控下,出水DON浓度-出水DON生物有效性-微生物生理生化特性和群落结构之间的相关关系,使用RDA对前述结果 (出水DON浓度、DON生物有效性、微生物生理生化特性、微生物群落结构) 进行深入分析,结果如图7所示。由图7可知,RD1与RD2分别代表了62.4%与10.9%的总差异,对于原始数据解释度大于70%,表明通过冗余分析,原始数据中的变化规律即相关关系仍然得到了较为完整的数据保留,并在一定程度上有映射到RDA二维分析图中。DON和ABDON浓度与外源添加钙离子浓度呈显著负相关,这再一次地证明了,外源添加钙离子对于提高DON去除率、降低DON生物有效性具有积极作用。在外源钙离子的调控下,5组反应器对应的样点表现出显著的组内聚类以及组外分离现象。该现象表明,在钙离子的作用下,5组反应器在微生物生理生化特性和群落结构方面表现出一定统计学意义的差异,这种差异与钙离子浓度以及出水DON浓度之间具有较强的相关性。因此,综合外源钙离子浓度、出水DON浓度、出水DON生物有效性、微生物生理生化特性、微生物群落结构分析结果,冗余分析进一步解释了在外加钙离子调控好氧活性污泥系统中DON去除过程中,微生物扮演了重要的介导传递作用。
-
1) 外加钙离子对于好氧活性污泥系统去除DON的调控效果具有积极作用,但其强化系统DON去除能力的作用具有阈值。外源钙离子投加最佳取值为0.1 mmol·L−1,在此条件下,可进一步降低33.3%的出水DON浓度,降低DON生物有效性47.6%。
2) DON分子组成分析得到的最佳钙离子投加条件与DON生物有效性一致,表明外加钙离子是通过影响好氧活性污泥反应器中氧化程度较低分分子 (NOSC<0) 影响了出水DON的生物有效性,从而调控出水DON的富营养化潜能。
3) 微生物学分析表明,在外源钙离子最佳取值的条件下,系统中ATP、SDH酶、DHA酶这类与微生物代谢密切相关的生物酶活达到较高水平,使得微生物对于有机物降解代谢能力有效提高。同时,微生物细胞膜中饱和脂肪酸相对丰度增加至64.79%,有效降低细胞膜流动状态,减少了微生物代谢DON的排放。微生物群落中发挥有机物降解作用的Luteolibacter菌在外源钙离子最佳取值的条件下富集至7.44%,是推动DON去除率提升的重要因素。
4) 冗余分析表明了不同外加钙离子浓度下好氧活性污泥微生物在生理特征和群落结构上的显著差异,再次阐明了微生物在影响出水DON浓度和生物有效性过程中的重要介导作用。
外源钙离子对好氧活性污泥反应器溶解性有机氮特征的影响
Effect of exogenous calcium ions on characteristics of dissolved organic nitrogen in aerobic activated sludge reactors
-
摘要: 为探明外源钙离子对好氧活性污泥系统溶解性有机氮 (DON) 的影响,考察了不同钙离子浓度下 (0~1 mmol·L−1) 出水DON浓度和生物有效性的变化,并结合傅里叶变换离子回旋共振质谱 (FTICR-MS) 及微生物代谢活性和群落结构分析探究钙离子影响的分子层面原因和微生物内在机理。结果表明,出水DON的浓度和生物有效性随着外源钙离子浓度的增加均呈现阈值现象,在最佳钙离子投加阈值浓度 (0.1 mmol·L−1 Ca2+) 下,出水DON浓度和生物有效性为1.46±0.12 mg·L−1和17.97%±0.05%,比空白组 (0 mmol·L−1 Ca2+) 分别增加了35.2%和降低了47.6%。FTICR-MS分析DON的分子特征显示,钙离子是通过影响好氧活性污泥反应器中氧化程度较低分的组分 (NOSC<0) 影响了最终出水DON的生物有效性。微生物学分析表明,三磷酸腺苷、琥珀酸脱氢酶、脱氢酶、饱和脂肪酸和Luteolibacter菌是推动出水DON去除率提升和生物有效性降低的重要因素。
-
关键词:
- 钙离子 /
- 溶解性有机氮(DON) /
- 生物有效性 /
- 傅里叶变换离子回旋共振质谱
Abstract: To investigate the effect of exogenous calcium ions on dissolved organic nitrogen (DON) in aerobic activated sludge systems, this study examined the changes in effluent DON concentration and bioavailability under different calcium ion concentrations (0~1 mmol·L-1). Fourier transform ion cyclotron resonance mass spectrometry (FTICR-MS) and microbial analysis of metabolic activity and commol·L-1unity structure were combined to explore the molecular reasons and microbial mechanisms underlying the influence of calcium ions. The results showed that both the effluent DON concentration and bioavailability exhibited threshold phenomena with increasing exogenous calcium ion concentration, reaching 1.46±0.12 mg·L−1 and 17.97±0.05% at the optimal calcium ion dosage threshold (0.1 mmol·L-1). At this dosage, the DON concentration and bioavailability increased by 35.2% and decreased by 47.6% compared to the blank group (0 mmol·L-1), respectively. FTICR-MS analysis of DON molecular characteristics showed that calcium ions influenced the final effluent DON bioavailability mainly by affecting the less oxidative DON components (NOSC<0) in the aerobic activated sludge bioreactor. Microbiological analysis indicated that ATP, SDH, DHA, saturated fatty acids, and Luteolibacter were important factors promoting the increase in DON removal and decrease in effluent DON bioavailability. -
城市污水排放是地表水最重要的人为氮源污染之一[1]。近年来,为了更好地调控受纳水体的富营养化风险,污水处理厂的总氮排放标准越来越严格,包括美国、欧洲和中国的部分地区甚至要求出水达到超低总氮排放限值 (5~10 mg·L−1) [2]。除了溶解性无机氮 (即氨氮、硝态氮和亚硝态氮) ,溶解性有机氮 (DON) 作为污水处理厂重要的出水氮组分越来越受到关注。特别是在无机氮脱除技术不断提标以及总氮排放限值愈发严苛的背景下,DON在污水总氮中的占比越来越高 (>65%) [3]。以往的研究表明,DON是一种潜在的生物可利用氮源,相当一部分DON可以很容易的被藻类和细菌利用[4]。EAM等[5]研究发现DON表现出比无机氮更强的刺激浮游植物生长的能力。目前常使用可以支持藻类生长的DON占总DON的比例来代表DON的生物有效性,用以表征污水DON的富营养化潜能[6-7]。活性污泥法是污水处理厂中最广泛应用的技术,其中好氧活性污泥法比厌氧和缺氧活性污泥法更容易导致较高的出水DON浓度[8]。因此,探讨调控好氧活性污泥法中DON的技术方法,尤其是从生物有效性的角度,对于有效保护受纳水体水质具有重要的意义。
投加外源金属二价阳离子 (如Mg2+、Ca2+、Fe2+、Mn2+) 可以通过影响微生物的表面电荷分布,酶活性等方式影响活性污泥系统的水处理能力影响出水水质[9]。例如,ZHANG等[10]研究发现投加镁离子 (Mg2+) 浓度低于1.1 mmol·L−1时,好氧活性污泥硝化活性显著提高,但在镁离子浓度达到3 mmol·L−1时硝化活性受到抑制。SINDHU等[11]在厌氧氨氧化系统中发现亚铁离子 (Fe2+) 添加对污泥胞外聚合物产量和脱氮效果有很大影响,当添加1 mmol·L−1 Fe2+时,氨氮和硝态氮去除率可以分别达到94.33%和94.84%。樊艳丽等[12]发现钙离子 (Ca2+) 会影响活性污泥系统的总氮 (TN) 去除率。所以投加适量外源金属离子常被用作强化好氧活性污泥处理性能的方法。其中,Ca2+被发现可以能够影响污泥的代谢产物,如胞外聚合物 (EPS) 和微生物溶解性产物 (SMP) 。这些代谢产物主要是蛋白质和多糖,与污水中的DON直接相关。ZHANG等[13]发现投加168.5 mg·L−1的钙离子能够有效减少微生物絮体中松散结合的EPS和上清液中SMP。ARABI和NAKHLA[14]也在140 mg·L−1的钙离子投加量下发现了污泥上清液中SMP的降低。综上表明,向活性污泥系统适量投加钙离子具有调控出水DON的潜力。然而,目前对于钙离子对好氧活性污泥DON的影响及内在微生物作用机理仍不明确。
本研究旨在探究外源钙离子对好氧活性污泥DON及其生物有效性的影响,并基于超高分辨率的傅里叶变换离子回旋共振质谱 (FTICR-MS) 分析DON的分子特征,解释其生物有效性变化的原因。最后,通过分析微生物的生理变化特征及群落结构尝试从微生物角度阐释钙离子影响好氧活性污泥DON的内在机理。本研究的结果将为污水处理厂中好氧活性污泥法的出水DON控制提供实践指导,以更好地调控出水氮的富营养化潜能,降低污水排放对于水环境的负面影响。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 实验装置与运行
本研究以钙离子浓度为外源物质,设置钙离子浓度水平为0.01、0.05、0.1以及1 mmol·L−1为实验组、钙离子浓度水平为0 mmol·L−1为对照组,探究外源投加钙离子对好氧活性污泥DON去除效果的影响。采用实际废水 (市政污水厂一级处理出水) 作为进水,本研究中进水的COD是126.73~172.38 mg·L−1、TN浓度是29.74~44.07 mg·L−1、TP浓度是2.51~3.27 mg·L−1、DON浓度是7.94~12.32 mg·L−1。当地的市政污水厂一级出水的DON浓度也基本在5.94~13.92 mg·L−1范围内,这表明本研究的进水有机氮水平具有代表性。本研究通过外加CaCl2调节水中钙离子浓度,每个浓度水平设置2个平行,搭建好氧活性污泥反应器。监测指标为反应器出水中的基本水质参数 (COD、无机氮各项指标、DON) 、DON分子组成以及微生物特性。反应器运行3个SRT后各项基本水质指标趋于稳定。
1.2 常规水质指标及DON浓度测定
化学需氧量 (COD) 采用快速密闭催化消解法测定[15]。DON的浓度表示为总溶解氮 (TDN) 减去所有的无机氮,包括氨氮 (NH4+-N) 、硝态氮 (NO3−-N) 和亚硝态氮 (NO2−-N) 。TDN测定通过过硫酸盐消化法将样品氧化成NO3−-N,然后采用离子色谱法定量NO3−-N的浓度[16]。NH4+-N采用水杨酸法进行测定。NO3−-N和NO2−-N使用离子色谱法 (Dionex ICS-1100,美国赛默飞世尔科技有限公司) 进行测定[16]。
1.3 DON生物有效性测定
首先采用14 d藻类生物培养实验测定可被藻类利用的DON (ABDON) 。选用中国科学院淡水藻种库 (FACHB-collection) 中被广泛用于水体富营养化表征的羊角月牙藻 (Selenastrum capricornutum) 作为测试藻种。将1.5 mL的藻类接种液和1 mL污水厂的混合培养菌添加到250 mL锥形瓶中的100 mL污水DON样品中。将锥形瓶置于22~25 ℃的温控摇床中培养,提供12 h∶12 h的光照:黑暗条件以模拟藻类生长真实环境条件[6]。用去离子水作为对照组。生物有效性的计算公式如式(1)和式(2)[17]。
ABDON(mg⋅L−1)=(DONi−DONf)−(DONbi−DONbf) (1) 生物有效性(%)=ABDONDON×100% (2) 式中:ABDON代表可被藻类利用的DON浓度,mg·L−1;DONi和DONf分别代表污水样品培养前后的DON浓度,mg·L−1;DONbi和DONbf分别代表去离子水样品培养前后的DON浓度,mg·L−1。
1.4 DON分子特征分析
所有的污水样品均采用PPL固相萃取柱来富集DON。在萃取之前,首先使用HPLC级的甲醇和盐酸溶液 (pH=2) 活化萃取柱。然后,将酸化后的水样 (pH=2,由盐酸调整) 以2 mg·min−1的流速通过PPL柱,随后使用pH=2的盐酸溶液冲洗柱子,并用氮气吹扫干燥[18]。最后,使用10mL甲醇对PPL柱进行洗脱[18]。洗脱液用甲醇稀释后以供进一步FTICR-MS分析。本研究采用15 T FTICR-MS (Bruker,德国布鲁克光谱仪器有限公司) ,配备负离子模式的电喷雾电离 (ESI) 源,分析样品中DON的分子组成。用注射泵将样品以180 μL·h−1的流速注入ESI源。使用Bruker数据分析软件 (v.4.1) 对原始峰进行识别,筛选出质量在200~700 m/z范围内信噪比S/N>6的峰进行分子式计算[19]。分子式根据以下元素进行分配:碳 (C,2~50) 、氧 (O,0~30) 、氢 (H,2~120) 、氮 (N,0~6) 、磷 (P,0~2) 和硫 (S,0~2) 。原子数量之间必须满足2≤H≤(2C+2)、O≤(C+2)、O/C<1.2、0.333≤H/C≤2.25、N/C<0.5、S/C<0.2、P/C<0.1、(S+P)/C<0.2、P<O/3,用以排除极不可能在DON中出现的分子式。本研究采用不饱和等效双键数 (DBE) 和碳的平均氧化态 (NOSC) 来表征DON的分子特征,计算公式如式(3)和式(4)[20]。
DBE=2C+N+P−H+22 (3) NOSC=4−4C+H−2O−3N−2S+5PC (4) 1.5 微生物活性测试
本研究选择三磷酸腺苷 (ATP) 、琥珀酸脱氢酶 (SDH) 、脱氢酶 (DHA) 、比耗氧速率 (SOUR) 探究不同外源钙离子浓度下好氧活性污泥的微生物活性[21]。ATP浓度使用 BacTiter-Glo™ 微生物细胞活性检测试剂盒进行测定[22]。SDH活性采用琥珀酸脱氢酶活性比色测定试剂盒测定,SDH的最终浓度通过BCA蛋白质测定试剂盒测量的蛋白质浓度进行标准化[21]。DHA活性通过测量 2,3,5-三苯基氯化四氮唑 (TTC) 还原成三苯基甲臜 (TPF) 的量来测定[23]。SOUR通过使用溶解氧测量仪测定一定时间内好氧活性污泥的耗氧量进行计算。另外,本研究还通过测定微生物细胞膜上磷脂脂肪酸 (PLFA) 的变化知识微生物活动的变化。PLFA分析依据NIU等[24]提供的方法进行,包括分离、洗脱、萃取和皂化甲基化。使用固相萃取柱分离得到磷脂,皂化甲基化后的脂肪酸甲酯采用气相色谱仪 (Agilent 7890,美国安捷伦科技有限公司) 测定,最后使用MIDI Sherlock微生物鉴定系统对结果进行分析。
1.6 微生物群落结构分析
从好氧污泥反应器中各收集3个平行的污泥样本,使用 FastDNA土壤试剂盒对s6个反应器中的污泥进行 DNA 提取。然后,DNA提取物被送往上海生工生物工程技术服务有限公司进行16S rRNA基因PCR扩增,PCR产物纯化和随后的Illumina MiSeq测序[25]。最后,使用Mothur软件包 (v.1.35.1) 进行数据分析[26]。
1.7 数据统计分析
采用SPSS统计软件进行显著性差异分析 (单因素方差分析,ANOVA) ,当p值为<0.05认为是差异是显著的。冗余分析 (RDA) 使用CANOCO 4.5软件进行,用以探讨DON浓度及特征与微生物之间的相关关系[25]。
2. 结果与讨论
2.1 DON浓度和生物有效性
通过对比5组反应器出水DON浓度,可探究外加钙离子对于好氧活性污泥反应器DON去除效率的影响。由图1可知,随着外加钙离子浓度的增加,反应器出水DON的浓度表现出先降低后增加的趋势。其中,空白组出水DON浓度为(2.19±0.18) mg·L−1 (0 mmol·L−1,Ca2+) ,当外加钙离子浓度为0.01~1 mmol·L−1,出水DON浓度为1.46~2.13 mg·L−1。增效阈值的现象存在于外加钙离子对于好氧活性污泥去除DON的作用中。对于本研究中设定实验条件,外加钙离子对于提高好氧活性污泥反应器DON去除效果的阈值为0.1 mmol·L−1,此时出水DON浓度为1.46±0.12 mg·L−1, 出水DON浓度相比于空白组降低了33.3%。当外加钙离子浓度低于0.1 mmol·L−1,随着钙离子浓度增加,出水DON浓度降低;当外加钙离子浓度高于0.1 mmol·L−1,随着钙离子浓度增加,出水DON浓度升高。同时,对比其他基本出水水质指标可知,外加钙离子在其中的增效作用阈值同样为0.1 mmol·L−1。TANG等[27]研究在微藻-细菌共生系统中也观察到相似的结果,较低的钙离子 (Ca2+) 负荷 (即0.1 mmol·L−1) 可以促进中COD和营养物质的去除。因此,对于基本水质以及出水DON浓度而言,0.1 mmol·L−1的外加钙离子浓度是提高好氧活性污泥反应器处理性能的最佳取值。
如图2所示,出水生物DON的生物有效性与DON浓度随外加钙离子浓度的增加先降低后增加,也呈现出相似的阈值现象。空白组出水DON有效性为34.29%±0.06% (0 mmol·L−1,Ca2+) 。当外加钙离子浓度为从0.01 mmol·L−1增加到0.1 mmol·L−1时,好氧活性污泥出水的DON生物有效性从30.60%±0.05%降低至17.97%±0.05%;当外加钙离子浓度提高到0.1 mmol·L−1时,DON的生物有效性又提高至18.54%±0.04%。生物有效性DON基于藻类生长表征DON的富营养化潜能,能够更加直接地呈现外加钙离子对于好氧活性污泥反应器出水对于自然水体水质的影响[28]。因此上述结果表明,对于本研究的实验条件,基于DON的生物有效性,0.1 mmol·L−1仍是外源钙离子对于降低好氧活性污泥反应器DON生物有效性、管控DON富营养化潜能排放的最佳阈值浓度,此时DON的生物有效性相比于空白组降低了47.6%。值得讨论的是,城市污水处理厂中的一般本底钙离子浓度为30~60 mg·L−1 (0.75~1.5 mmol·L−1) [29]。本研究中0.1 mmol·L−1的钙离子最佳投加浓度阈值对于体系造成的改变并不算是极少的。因此,在考虑了实际污水处理厂的本底钙离子浓度水平后,本研究中所应用的外源钙离子浓度仍然具有能够显著影响好氧活性污泥系统的潜力。
2.2 DON分子组成
DON的生物有效性与它的分子化学性质密切相关[30]。为了从分子层面解析外加钙离子对好氧活性污泥反应器出水DON生物有效性的影响,采用FTICR-MS进一步分析DON的分子组成特征 (图3) 。NOSC通常用来反应分子的氧化还原状态,而氧化还原状态已经被证实与微生物活动密切相关[31]。已有研究指出,低平均碳氧化态的DON分子 (NOSC<0) 主要包括氨基酸、脂质、蛋白质和不饱和烃[32],这些分子更容易被藻类微生物降解利用[33],因此是高生物有效性的组分。ZHANG等[18]在研究中发现NOSC与难降解的芳香化合物 (用SUVA254指示) 和类腐殖酸呈现负相关,这也侧面证实了低NOSC的分子可能更加容易生物降解。因此,本研究选择NOSC<0的分子代表高生物有效性的分子。
如图3所示,不同外加钙离子浓度下,好氧活性污泥的DON分子均主要分布在NOSC<0的高生物有效性区域。这与HUO等[8]在A/A/O工艺中关于好氧活性污泥产生更多容易降解的微生物代谢DON的推测一致。韩成龙等[15]也发现好氧段出水中易生物降解的DON占比更高。此外,好氧活性污泥反应器出水中NOSC<0的DON分子数量随外加钙离子浓度变化的趋势与由藻类直接测定的生物有效性变化相同,呈现先减少后增加的趋势,且阈值同样出现在0.1 mmol·L−1 (图3) 。空白组出水DON中位于高生物有效性区域的分子最多 (0 mmol·L−1,Ca2+) 。当外加钙离子浓度在0~0.1 mmol·L−1范围内逐渐增加时,NOSC<0的DON分子逐渐减少;当外加钙离子浓度大于0.1 mmol·L−1时,NOSC<0的DON分子增加。因此可以合理推断外加钙离子通过影响好氧活性污泥反应器中氧化程度较低的分子 (NOSC<0) 影响DON的生物有效性,从而调控出水DON的富营养化潜能。
2.3 微生物生理生化特征及微生物群落结构
在好氧活性污泥系统中,DON的去除依赖活性污泥微生物的降解与转化作用。并且,已有研究探明,适量浓度的外加钙离子可以增加活性污泥系统的TN去除能力[12]。微生物在好氧活性污泥脱氮的过程中扮演着关键角色,介导了外加钙离子对于DON浓度的影响。出水DON是出水TN的重要组成部分,因此可从微生物学角度进行阐述外加钙离子调控DON去除过程的机理。据已有研究报道,外加钙离子可通过改变微生物活性、驯化相应的微生物、促进微生物群落的演替,从而改变系统中微生物的水处理能力,进而改变出水水质[34]。其中,微生物活性涉及微生物酶活、微生物活性物质,或其他可指代微生物活性的相关指标,如ATP、DHA酶活、SDH酶活、SOUR等[21, 23]。本研究通过分析不同外加钙离子浓度下微生物活性的变化以及微生物群落结构的演替,解析外加钙离子调控DON去除过程的内在机理。
微生物ATP测试结果如图4(a)所示,空白组中,ATP浓度为(10.32±0.93) μg· (g MLSS) −1;实验组中,随着外加钙离子浓度逐渐升高,ATP浓度出现先增后减趋势,ATP浓度分别为(12.35±0.55) μg· (g MLSS) −1 (0.01 mmol·L−1 Ca2+) 、(17.02±0.79) μg· (g MLSS) −1 (0.05 mmol·L−1 Ca2+) 、(16.62±0.21) μg· (g MLSS) −1 (0.1 mmol·L−1 Ca2+)、(8.97±0.92) μg· (g MLSS) −1 (1 mmol·L−1 Ca2+) 。对比空白组与实验组结果可知,外加钙离子对于ATP的作用同样具有阈值效应。ATP是为微生物生长代谢过程提供能量的物质,一定程度上ATP浓度的升高可表明微生物生长代谢活动的增加,因此活性污泥中ATP的浓度可指示微生物活性的高低[35]。升高的ATP表明外加钙离子可在一定程度上提高微生物的代谢活性。
SDH酶、DHA酶与ATP相似,是表征微生物代谢活性过程中常见的指示物质。如图4(b)所示,SDH酶浓度为(16.89±0.67) U· (mg protein)−1 (0 mmol·L−1,Ca2+)、(22.01±1.08) U· (mg protein)−1 (0.01 mmol·L−1,Ca2+)、(24.49±0.81) U· (mg protein)−1 (0.05 mmol·L−1,Ca2+)、(26.95±2.11) U· (mg protein)−1 (0.1 mmol·L−1,Ca2+) 、(14.42±0.64) U· (mg protein)−1 (1 mmol·L−1,Ca2+) ,结果表明外源钙离子添加浓度为0.05~0.1 mmol·L−1时,SDH酶活较高、微生物代谢能力较强。该结果显示的钙离子浓度的阈值 (0.1 mmol·L−1) 与本研究中好氧活性污泥的DON浓度和DON生物有效性所呈现的阈值一致。SDH酶是三羧酸循环中的关键酶,可作为评价三羧酸循环的指标[36]。已有研究表明生物有效性的DON包括氨基酸、脂质等分子,而三羧酸循环作为糖类、脂类和氨基酸的最终代谢通路[37],能够影响微生物对这部分DON的去除。因此SDH酶活变化一定程度上反映了出水DON生物有效性变化的原因。另外注意到,SDH酶活性与ATP浓度随钙离子浓度变化的趋势类似,但外加钙离子对于SDH酶活的阈值为0.1 mmol·L−1,而对于ATP的阈值为0.05 mmol·L−1,二者略有区别。这种阈值的差别可能与两种酶在微生物代谢过程中的功能差异相关。另一方面,微生物降解污染物时,有机物在微生物细胞中的氧化作用一般通过脱氢作用获得能量,DHA酶是微生物代谢过程发挥作用的重要生物酶[38]。如图4(d)所示,DHA酶在外加钙离子浓度为0.05 mmol·L−1时,具有最大活性,为(7.17±0.22) mg TF·(g MLSS) −1。总体而言,随着外加钙离子浓度升高,3种生物酶活性变化趋势相近,均为活性先增加至某一阈值后降低。这表明,外加钙离子可能通过影响与微生物代谢活动有关的酶活性影响到DON,尤其是生物有效性DON的去除。
在现有研究中,常使用SOUR表示单位时间内单位质量活性污泥消耗氧气的体积。在好氧活性污泥系统中,好氧微生物氧化有机物产能代谢的过程主要是以氧气作为最终电子受体。因此相应地,SOUR数值的大小也可直接反映好氧活性污泥系统中微生物活动的变化[39]。如图4(c)所示,随着外加钙离子浓度由0.01 mmol·L−1增加至0.1 mmol·L−1,SOUR数值逐渐上升;当外加钙离子浓度增加至1 mmol·L−1,SOUR数值虽略有下降,但与钙离子浓度为0.1 mmol·L−1时无统计学意义的差别 (p>0.05,ANOVA) 。SOUR与DON浓度和生物有效性相近的阈值现象也进一步证明了外加钙离子导致的DON浓度及DON生物有效性的变化与微生物代谢有机物的活性密切相关。综上所述,一定浓度的外加钙离子能够提高好氧活性污泥中微生物的代谢活性,通过增强微生物对有机物的氧化代谢提高有机物的去除率,从而降低了好氧出水的DON。张兰河等[40]也在研究中发现适量外源钙离子的投加提高了活性污泥体系中DHA酶活性和SOUR。虽然外源钙离子在提高微生物代谢活性的同时增加了EPS的合成,但带正电的钙离子可以与EPS表面带负电的官能团形成架桥,二者的络合不仅提高了污泥的絮凝沉降性能,也使得松散结合型EPS的比例 (LB-EPS/EPS) 降低[40-41]。由于LB-EPS与SMP的形成密切关联[13],且SMP中由微生物产生的蛋白质等物质又是生物有效性DON的重要组成部分,因此钙离子与EPS的络合作用也一定程度上支持了本研究中适量外源钙离子促进出水DON影响浓度及生物有效性降低的发现。
除了生物酶活,微生物细胞膜的组成也可以作为辅助指标指示微生物活性的变化。PLFA是微生物细胞膜磷脂双分子层的主要组成部分,多存在于活性微生物中,微生物死亡后PLFA会被迅速降解。并且PLFA可进一步分类为饱和脂肪酸 (SFA) 、不饱和脂肪酸 (UFA) 、异构脂肪酸 (IFA) 和反式异构脂肪酸 (AFA) [42]。图5展示了不同外加钙离子浓度对微生物细胞膜的影响。结果表明,5组反应器中,饱和脂肪酸 (SFA) 在细胞膜组成中相对丰度由大到小为:外加钙离子浓度为0.1 mmol·L−1时 (69.91%) >外加钙离子浓度为0.05 mmol·L−1时 (64.79%) >外加钙离子浓度为1 mmol·L−1时 (62.35%) >外加钙离子浓度为0.01 mmol·L−1时 (56.40%) >空白组(55.37%)。不饱和脂肪酸 (UFA) 在细胞膜组成中相对丰度由大到小为:空白组 (28.79%) >外加钙离子浓度为0.01 mmol·L−1时 (26.58%) >外加钙离子浓度为0.05 mmol·L−1 (24.95%) >外加钙离子浓度为1 mmol·L−1时 (22.79%) >外加钙离子浓度为0.1 mmol·L−1时 (20.69%) 。细胞膜组成中的饱和脂肪酸与不饱和脂肪酸是评价细胞膜流动性的重要指标。已有研究报道,微生物在环境影响下会自发改变细胞膜PLFA组成,通过调节饱和脂肪酸/不饱和脂肪酸在细胞膜中的占比调节细胞膜流动性[42]。基于不同外加钙离子浓度下好氧活性污泥反应器中DON浓度的变化结果,外加钙离子浓度为0.1 mmol·L−1为提高好氧活性污泥反应器去除DON效率的最佳取值。当外加钙离子浓度为0.1 mmol·L−1时细胞膜饱和脂肪酸占比最高 (64.79%),不饱和脂肪酸 (20.69%) 和反式异构脂肪酸占比最低 (5.12%) 。在微生物细胞膜组成中,反式异构脂肪酸具有与不饱和脂肪酸相同的作用,通过破坏磷脂酰基链的紧密堆积从而改变细胞膜流动性[43-44]。因此,反式异构脂肪酸在细胞膜中相对丰度增加,会提高细胞膜流动性。据报道,细胞膜的流动性极大地影响了微生物胞内许多与结构或功能无关的化合物的运输和排出,这可能对微生物代谢的DON产物的释放产生重要影响[45-46]。MA等[45]研究表明细胞流动性越低,出水蛋白质含量越低。在本研究中,出水DON浓度和生物有效性最低时 (外加钙离子浓度为0.1 mmol·L−1) ,细胞膜组成的分析结果都表明了细胞膜组成转变为流动性更低的状态,这可能阻滞了微生物代谢产生的DON的排放,从而使得在该浓度下能达到最佳的出水DON排放浓度和生物有效性。
微生物群落结构是影响好氧活性污泥系统水处理效果的重要因素之一。因此,对比5组反应器在不同外加钙离子浓度下微生物群落结构的变化,可进一步解析最优钙离子投加条件下 (外加钙离子浓度为0.1 mmol·L−1) 促使DON去除效率最高的原因。图6展示了5组反应器在稳定期微生物群落在属水平的分布。除尚无对应分类名录的菌种外,在属水平上的主要微生物菌种 (按照5组反应器中相对丰度值由大到小) 为Saccharibacteria_genera_incertae_sedis、Propionicicella、Luteolibacter、Ferruginibacter、Defluviimonas、Dechloromonas、Rhodoferax、Blastocatella、Sphingorhabdus、Ferribacterium等。其中值得注意的是,Luteolibacter为微生物群落中发挥降解有机物作用的好氧菌[47],是指示微生物群落对有机物去除能力的重要菌种。对比不同外加钙离子浓度下Luteolibacter菌的相对丰度变化可知,当外加钙离子浓度由0.01 mmol·L−1增加至0.1 mmol·L−1时,Luteolibacter菌相对丰度由2.07%富集至7.44%;当外加钙离子浓度由0.1 mmol·L−1增加至1 mmol·L−1时,Luteolibacter菌相对丰度下降至3.56%。这说明Luteolibacter菌在钙离子调控的环境下,其存活状态同样具有生存阈值,在一定范围内,外加钙离子可通过富集时Luteolibacter菌强化系统对有机物去除的能力,从而提高DON去除率。一定程度而言,在外加0.1 mmol·L−1钙离子调控好氧活性污泥系统的DON去除过程中,Luteolibacter菌扮演着不可忽视的作用。因此,外源钙离子可能通过调整微生物群落结构,尤其是提高降解有机物的好氧菌的相对丰度,强化对于好氧活性污泥反应器中DON的去除。
进一步地,为揭示在外源钙离子调控下,出水DON浓度-出水DON生物有效性-微生物生理生化特性和群落结构之间的相关关系,使用RDA对前述结果 (出水DON浓度、DON生物有效性、微生物生理生化特性、微生物群落结构) 进行深入分析,结果如图7所示。由图7可知,RD1与RD2分别代表了62.4%与10.9%的总差异,对于原始数据解释度大于70%,表明通过冗余分析,原始数据中的变化规律即相关关系仍然得到了较为完整的数据保留,并在一定程度上有映射到RDA二维分析图中。DON和ABDON浓度与外源添加钙离子浓度呈显著负相关,这再一次地证明了,外源添加钙离子对于提高DON去除率、降低DON生物有效性具有积极作用。在外源钙离子的调控下,5组反应器对应的样点表现出显著的组内聚类以及组外分离现象。该现象表明,在钙离子的作用下,5组反应器在微生物生理生化特性和群落结构方面表现出一定统计学意义的差异,这种差异与钙离子浓度以及出水DON浓度之间具有较强的相关性。因此,综合外源钙离子浓度、出水DON浓度、出水DON生物有效性、微生物生理生化特性、微生物群落结构分析结果,冗余分析进一步解释了在外加钙离子调控好氧活性污泥系统中DON去除过程中,微生物扮演了重要的介导传递作用。
3. 结论
1) 外加钙离子对于好氧活性污泥系统去除DON的调控效果具有积极作用,但其强化系统DON去除能力的作用具有阈值。外源钙离子投加最佳取值为0.1 mmol·L−1,在此条件下,可进一步降低33.3%的出水DON浓度,降低DON生物有效性47.6%。
2) DON分子组成分析得到的最佳钙离子投加条件与DON生物有效性一致,表明外加钙离子是通过影响好氧活性污泥反应器中氧化程度较低分分子 (NOSC<0) 影响了出水DON的生物有效性,从而调控出水DON的富营养化潜能。
3) 微生物学分析表明,在外源钙离子最佳取值的条件下,系统中ATP、SDH酶、DHA酶这类与微生物代谢密切相关的生物酶活达到较高水平,使得微生物对于有机物降解代谢能力有效提高。同时,微生物细胞膜中饱和脂肪酸相对丰度增加至64.79%,有效降低细胞膜流动状态,减少了微生物代谢DON的排放。微生物群落中发挥有机物降解作用的Luteolibacter菌在外源钙离子最佳取值的条件下富集至7.44%,是推动DON去除率提升的重要因素。
4) 冗余分析表明了不同外加钙离子浓度下好氧活性污泥微生物在生理特征和群落结构上的显著差异,再次阐明了微生物在影响出水DON浓度和生物有效性过程中的重要介导作用。
-
-
[1] PRICE J R, LEDFORD S H, RYAN M O, et al. Wastewater treatment plant effluent introduces recoverable shifts in microbial community composition in receiving streams[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2018, 613-614: 1104-1116. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.09.162 [2] CHENG H Z, MA S J, LIAO K W, et al. Effect of external carbon source type on effluent dissolved organic nitrogen characteristics in postdenitrifying moving bed biofilm reactors: Chemical molecular and microbial insights[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2023, 466: 143338. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2023.143338 [3] PEHLIVANOGLU-MANTAS E, SEDLAK D L. Wastewater-derived dissolved organic nitrogen: analytical methods, characterization, and effects—A review[J]. Critical Reviews in Environmental Science and Technology, 2006, 36(3): 261-285. doi: 10.1080/10643380500542780 [4] LIU H Z, JEONG J, GRAY H, et al. Algal uptake of hydrophobic and hydrophilic dissolved organic nitrogen in effluent from biological nutrient removal municipal wastewater treatment systems[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2012, 46(2): 713-721. [5] EOM H, BORGATTI D, PAERL H W, et al. Formation of low-molecular-weight dissolved organic nitrogen in predenitrification biological nutrient removal systems and its impact on eutrophication in coastal waters[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2017, 51(7): 3776-3783. [6] HU H D, LIAO K W, GENG J J, et al. Removal characteristics of dissolved organic nitrogen and its bioavailable portion in a postdenitrifying biofilter: Effect of the C/N ratio[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2018, 52(2): 757-764. [7] PEHLIVANOGLU E, SEDLAK D L. Bioavailability of wastewater-derived organic nitrogen to the alga Selenastrum Capricornutum[J]. Water Research, 2004, 38(14): 3189-3196. [8] HUO S L, XI B D, YU H L, et al. Characteristics and transformations of dissolved organic nitrogen in municipal biological nitrogen removal wastewater treatment plants[J]. Environmental Research Letters, 2013, 8(4): 044005. doi: 10.1088/1748-9326/8/4/044005 [9] 何甦. 低温好氧污泥活性的影响因素研究[D]; 江苏: 南京大学, 2020. [10] ZHANG L H, ZHAO Q N, ZHANG M S, et al. Mg2+ distribution in activated sludge and its effects on the nitrifying activity and the characteristics of extracellular polymeric substances and sludge flocs[J]. Process Biochemistry, 2020, 88: 120-128. doi: 10.1016/j.procbio.2019.10.002 [11] SINDHU L, NIU K L, LIU X L, et al. Effect of Fe2+ addition on anammox consortia, nitrogen removal performance and functional genes analysis during start-up of anammox process[J]. Journal of Water Process Engineering, 2021, 43: 102251. doi: 10.1016/j.jwpe.2021.102251 [12] 樊艳丽, 孔秀琴, 牛佳雪. 钙离子浓度对活性污泥处理系统脱氮效果的影响[J]. 石油学报(石油加工), 2014, 30(5): 921-927. [13] ZHANG H M, XIA J, YANG Y, et al. Mechanism of calcium mitigating membrane fouling in submerged membrane bioreactors[J]. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 2009, 21(8): 1066-73. doi: 10.1016/S1001-0742(08)62383-9 [14] ARABI S, NAKHLA G. Impact of cation concentrations on fouling in membrane bioreactors[J]. Journal of Membrane Science, 2009, 343(1): 110-118. [15] 韩成龙, 赵凌云, 段冰, 等. A2/O工艺中溶解性有机氮的分子转化与生物有效性特征[J]. 中国环境科学, 2023, 43(4): 1610-1619. [16] HU H D, LIAO K W, WANG J F, et al. Effect of influent carbon-to-nitrogen ratios on the production and bioavailability of microorganism-derived dissolved organic nitrogen (mDON) in activated sludge systems[J]. ACS ES& T Water, 2021, 1(9): 2037-2045. [17] HU H D, LIAO K W, SHI Y J, et al. Effect of solids retention time on effluent dissolved organic nitrogen in the activated sludge process: studies on bioavailability, fluorescent components, and molecular characteristics[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2018, 52(6): 3449-3455. [18] ZHANG B L, SHAN C, WANG S, et al. Unveiling the transformation of dissolved organic matter during ozonation of municipal secondary effluent based on FT-ICR-MS and spectral analysis[J]. Water Research, 2021, 188: 116484. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2020.116484 [19] HU H D, ZHU B Y, HAN L Q, et al. Effect of carrier filling ratios on dissolved organic nitrogen removal in integrated fixed-film activated sludge systems treating municipal wastewater[J]. ACS ES& T Engineering, 2021, 1(4): 761-769. [20] DU Y, DENG Y M, LIU Z H, et al. Novel insights into dissolved organic matter processing pathways in a coastal confined aquifer system with the highest known concentration of geogenic ammonium[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2021, 55(21): 14676-14688. [21] LIAO K W, HU H D, MA S J, et al. Effect of microbial activity and microbial community structure on the formation of dissolved organic nitrogen (DON) and bioavailable DON driven by low temperatures[J]. Water Research, 2019, 159: 397-405. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2019.04.049 [22] HAMMES F, GOLDSCHMIDT F, VITAL M, et al. Measurement and interpretation of microbial adenosine tri-phosphate (ATP) in aquatic environments[J]. Water Research, 2010, 44(13): 3915-3923. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2010.04.015 [23] FILIPIČ J, KRAIGHER B, TEPUŠ B, et al. Effects of low-density static magnetic fields on the growth and activities of wastewater bacteria Escherichia coli and Pseudomonas putida[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2012, 120: 225-232. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2012.06.023 [24] NIU C, GENG J J, REN H Q, et al. The strengthening effect of a static magnetic field on activated sludge activity at low temperature[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2013, 150: 156-162. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2013.08.139 [25] HU H D, MA S J, ZHANG X X, et al. Characteristics of dissolved organic nitrogen in effluent from a biological nitrogen removal process using sludge alkaline fermentation liquid as an external carbon source[J]. Water Research, 2020, 176: 115741. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2020.115741 [26] SCHLOSS PATRICK D, WESTCOTT SARAH L, RYABIN T, et al. Introducing mothur: open-source, platform-independent, community-supported software for describing and comparing microbial communities[J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2009, 75(23): 7537-3541. doi: 10.1128/AEM.01541-09 [27] TANG C, ZHANG X, WANG R, et al. Calcium ions-effect on performance, growth and extracellular nature of microalgal-bacterial symbiosis system treating wastewater[J]. Environmental Research, 2022, 207: 112228. doi: 10.1016/j.envres.2021.112228 [28] SATTAYATEWA C, PAGILLA K, PITT P, et al. Organic nitrogen transformations in a 4-stage Bardenpho nitrogen removal plant and bioavailability/biodegradability of effluent DON[J]. Water Research, 2009, 43(18): 4507-16. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2009.07.030 [29] LEE S H, YOO B H, KIM S K, et al. Enhancement of struvite purity by re-dissolution of calcium ions in synthetic wastewaters[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2013, 261: 29-37. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2013.06.072 [30] 汪杰, 郑芳, 柴文波, 等. 含氮有机物在污水处理过程中的生物转化机制与模型研究进展[J]. 微生物学通报, 2021, 48(5): 1717-1726. doi: 10.13344/j.microbiol.china.200797 [31] CORY R M, MCKNIGHT D M. Fluorescence spectroscopy reveals ubiquitous presence of oxidized and reduced quinones in dissolved organic matter[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2005, 39(21): 8142-8149. [32] YANG Y Y, TFAILY M M, WILMOTH J L, et al. Molecular characterization of dissolved organic nitrogen and phosphorus in agricultural runoff and surface waters[J]. Water Research, 2022, 219: 118533. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2022.118533 [33] MCDONOUGH L K, ANDERSEN M S, BEHNKE M I, et al. A new conceptual framework for the transformation of groundwater dissolved organic matter[J]. Nature Communications, 2022, 13(1): 2153. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-29711-9 [34] HUANG H, LIN Y, PENG P, et al. Calcium ion- and rhamnolipid-mediated deposition of soluble matters on biocarriers[J]. Water Research, 2018, 133: 37-46. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2018.01.010 [35] BREZONIK P L, PATTERSON J W. Activated sludge ATP: Effects of environmental stress[J]. Journal of the Sanitary Engineering Division, 1971, 97(6): 813-824. doi: 10.1061/JSEDAI.0001341 [36] HE S M, MCMAHON K D. ‘Candidatus Accumulibacter’ gene expression in response to dynamic EBPR conditions[J]. The ISME Journal, 2011, 5(2): 329-340. doi: 10.1038/ismej.2010.127 [37] ZHU L R, WU B C, LIU Y L, et al. Strategy to enhance semi-continuous anaerobic digestion of food waste by combined use of calcium peroxide and magnetite[J]. Water Research, 2022, 221: 118801. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2022.118801 [38] HAN Z S, TIAN J Y, LIANG H, et al. Measuring the activity of heterotrophic microorganism in membrane bioreactor for drinking water treatment[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2013, 130: 136-143. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2012.11.151 [39] LI K, QIAN J, WANG P F, et al. Toxicity of three crystalline TiO2 nanoparticles in activated sludge: bacterial cell death modes differentially weaken sludge dewaterability[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2019, 53(8): 4542-4555. [40] 张兰河, 王佳平, 陈子成, 等. Ca2+对序批式生物反应器活性污泥性能的影响[J]. 化工进展, 2018, 37(9): 3675-3681. [41] 张兰河, 赵倩男, 张海丰, 等. Ca2+对污泥硝化活性和絮凝沉降性能的影响[J]. 环境科学, 2019, 40(9): 4160-4168. [42] MA S J, DING L L, HUANG H, et al. Effects of DO levels on surface force, cell membrane properties and microbial community dynamics of activated sludge[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2016, 214: 645-652. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2016.04.132 [43] LOFFELD B, KEWELOH H. cis/trans isomerization of unsaturated fatty acids as possible control mechanism of membrane fluidity inPseudomonas putida P8[J]. Lipids, 1996, 31(8): 811-815. doi: 10.1007/BF02522976 [44] MURATA N, LOS D A. Membrane fluidity and temperature perception[J]. Plant Physiol, 1997, 115(3): 875-879. doi: 10.1104/pp.115.3.875 [45] MA S J, DING L L, HU H D, et al. Cell membrane characteristics and microbial population distribution of MBBR and IFAS with different dissolved oxygen concentration[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2018, 265: 17-24. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2018.03.111 [46] RAMOS J L, DUQUE E, GALLEGOS M-T, et al. Mechanisms of solvent tolerance in gram-negative bacteria[J]. Annual Review of Microbiology, 2002, 56(1): 743-768. doi: 10.1146/annurev.micro.56.012302.161038 [47] GARCíA A, VALENZUELA E I, VARGAS A, et al. Wastewater treatment potential, light penetration profile and biomass settling performance of a photo-sequencing batch reactor[J]. Journal of Chemical Technology & Biotechnology, 2023, 98(2): 346-356. 期刊类型引用(0)
其他类型引用(1)
-







 下载:
下载: