| 基于三维荧光光谱技术解析不同微生物法净化黑臭水体的效果 |
| |
| 引用本文: | 许瑞, 王胜楠, 陈乐, 王海珊, 戴犇, 邹平, 杨常亮, 王洁, 毕晓伊. 基于三维荧光光谱技术解析不同微生物法净化黑臭水体的效果[J]. 环境工程学报, 2020, 14(1): 123-132. doi: 10.12030/j.cjee.201903112 |
| |
| 作者姓名: | 许瑞 王胜楠 陈乐 王海珊 戴犇 邹平 杨常亮 王洁 毕晓伊 |
| |
| 作者单位: | 1.云南大学生态学与环境学院,昆明 650091; 2.云南大学国际河流与生态安全研究院,昆明 650091; 3.云南大学,国际河流与跨境生态安全重点实验室,昆明 650091; 4.云南大学,高原山地生态与退化环境修复重点实验室,昆明 650091 |
| |
| 摘 要: | 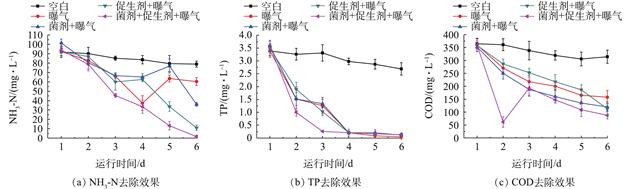
应用曝气、菌剂+曝气、生物促生剂+曝气、菌剂+生物促生剂+曝气4种微生物技术净化黑臭水体,分别考察了进水中溶解性有机物(DOM)的特征和来源及出水中DOM的特征和效果,采用三维荧光(EEM)光谱技术与平行因子(PARAFAC)模型相结合的方式对进出水DOM进行了分析。结果表明,不同处理方式下进出水DOM的不同组分荧光峰强度变化存在较明显的差异,经过菌剂和生物促生剂联合处理之后,对类腐殖质等难降解物质削减效果最好。FI、HIX和BIX指数分析表明各处理水样中的DOM整体处于较强的自生源特征。利用主成分分析法(PCA)对影响黑臭水体DOM的主要因素及其贡献量研究发现:第1主成分表现为陆源类腐殖质和生物源类腐殖质共存的现象,对水体中DOM的贡献率为54.98%;第2主成分反映了以微生物代谢过程为代表的内源污染,对水体中DOM的贡献率为26.56%。因此,利用三维荧光分析能够较好的反映水中DOM的去除情况,易于实时在线监测,对黑臭水治理具有重要意义。
|
| 关 键 词: | 黑臭水 微生物处理 溶解性有机物 三维荧光光谱 主成分分析 |
| 收稿时间: | 2019-03-16 |
| 本文献已被 CNKI 万方数据 等数据库收录! |
| 点击此处可从《环境工程学报》浏览原始摘要信息 |
|
点击此处可从《环境工程学报》下载免费的PDF全文 |
|

