| 基于浮游细菌生物完整性指数的城市河流健康评价:以深圳河流域为例 |
| |
| 引用本文: | 王力, 王丝可, 左剑恶, 李晓杰, 陈雨. 基于浮游细菌生物完整性指数的城市河流健康评价:以深圳河流域为例[J]. 环境工程学报, 2023, 17(6): 2007-2014. doi: 10.12030/j.cjee.202211054 |
| |
| 作者姓名: | 王力 王丝可 左剑恶 李晓杰 陈雨 |
| |
| 作者单位: | 1.清华大学深圳国际研究生院,深圳 518055;; 2.深圳职业技术学院,深圳 518055;; 3.清华大学环境学院,环境模拟与污染控制国家重点联合实验室,北京 100084 |
| |
| 基金项目: | 深圳市高等院校稳定支持计划 (WDZC20200819163549002) ;深圳市科创委可持续发展科技专项 (KCXFZ202002011008448) |
| |
| 摘 要: | 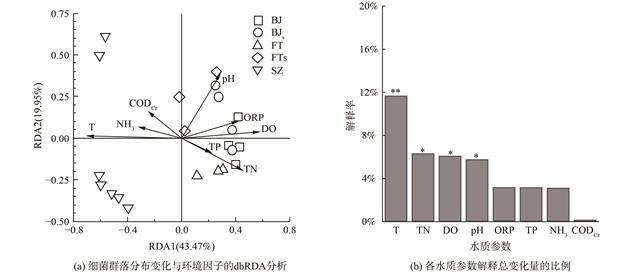
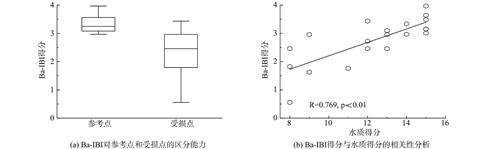
河流中的细菌是生态系统中物质循环的重要参与者,能反映河流健康状况,其群落生物指标具有评估城市河流生态状况的潜力。通过调查深圳河流域内深圳河、布吉河和福田河3条河流中的浮游细菌群落,构建了生物完整性指数 (Ba-IBI) ,评估了该流域的健康状况。基于河水浮游细菌的Illumina高通量测序结果,通过差异性检验、箱线图筛选和相关性分析方法从163个候选指标中筛选出变形菌门、放线菌门和微丝藻菌目相对丰度及门水平Simpson多样性指数作为核心指标,构建Ba-IBI评价体系。结果表明,深圳河流域内的20个位点中处于健康状态、亚健康状态、一般状态和较差状态的位点数分别为7个、4个、5个和4个。其中,深圳河处于一般和较差状态的点位比例高达85.7%;健康状况从上游到下游逐渐恶化;整体健康状况较差。布吉河和福田河健康状况相对较好,处于亚健康状态。各采样点Ba-IBI得分与水质状况的相关性较高 (R=0.77,P<0.01) ,表明Ba-IBI能有效评价城市河流的健康状况。本研究结果可为深圳市河流的修复和管理工作提供参考。
|
| 关 键 词: | 城市河流健康评价 生物完整性指数 浮游细菌 深圳河流域 |
| 收稿时间: | 2022-11-10 |
|
| 点击此处可从《环境工程学报》浏览原始摘要信息 |
|
点击此处可从《环境工程学报》下载免费的PDF全文 |
|


