| 低基质浓度下生物膜亚硝化工艺的快速启动及其运行效能 |
| |
| 引用本文: | 汪倩, 宋家俊, 郭之晗, 郭凯成, 刘文如, 沈耀良. 低基质浓度下生物膜亚硝化工艺的快速启动及其运行效能[J]. 环境工程学报, 2021, 15(7): 2512-2521. doi: 10.12030/j.cjee.202102098 |
| |
| 作者姓名: | 汪倩 宋家俊 郭之晗 郭凯成 刘文如 沈耀良 |
| |
| 作者单位: | 1.苏州科技大学环境科学与工程学院,苏州 215009; 2.江苏省水处理技术与材料协同创新中心,苏州 215009; 3.江苏省环境科学与工程重点实验室,苏州 215009 |
| |
| 基金项目: | 国家自然科学基金;江苏省研究生创新项目 |
| |
| 摘 要: | 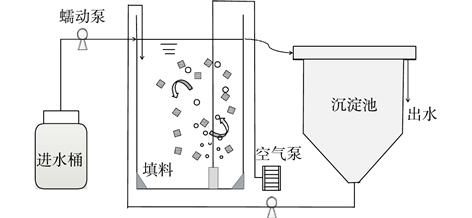
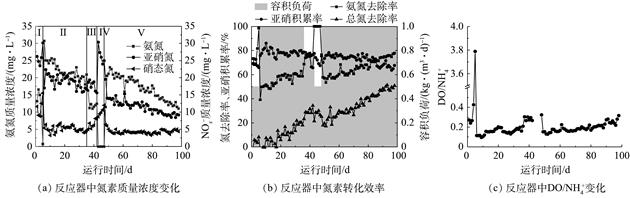
采用多孔凝胶填料,在低氨氮浓度下接种亚硝化絮体污泥进行填料挂膜,研究了反应器中填料的挂膜过程和不同DO/${{\rm{NH}}_{\rm{4}}^{\rm{ + }}}$下亚硝化效果,采用MiSeq高通量测序技术分析了反应器中微生物种群结构。结果表明:在初始的1~3 d,有大量悬浮絮体污泥进入填料内部,反应器中基本无絮体污泥;随后填料内部的微生物不断由内向外生长,填料表观颜色不断加深,30 d时填料挂膜成功;DO/$ {{\rm{NH}}_{\rm{4}}^{\rm{ + }}}$比值为0.09~0.2,氨氮容积负荷为1 kg·(m3·d)−1时,亚硝化效果最好,亚硝积累率最高达86.13%。随着DO/$ {{\rm{NH}}_{\rm{4}}^{\rm{ + }}}$的比值增加,亚硝积累率有所下降。
批次实验结果表明,通过控制DO/$ {{\rm{NH}}_{\rm{4}}^{\rm{ + }}}$的值,能够使生物膜表面形成一层耗氧屏障,则生物膜内部所能利用的氧有限,以此达到抑制NOB的目的。微生物分析结果表明:生物膜中AOB/NOB值为3,AOB在硝化细菌中占主导地位,生物膜中厌氧氨氧化菌得到富集,在34 d时丰度增加至25.13%,符合反应器总氮去除率上升的特征。
|
| 关 键 词: | 生物膜 亚硝化 厌氧氨氧化 DO/$ {{\rm{NH}}_{\rm{4}}^{\rm{ + }}}$ |
| 收稿时间: | 2021-02-20 |
| 本文献已被 万方数据 等数据库收录! |
| 点击此处可从《环境工程学报》浏览原始摘要信息 |
|
点击此处可从《环境工程学报》下载免费的PDF全文 |
|



