| 过氧化氢/磷钼酸体系的催化机制及对苯胺的降解效果 |
| |
| 引用本文: | 秦汉强, 肖博仁, 杨金星, 袁冬冬, 齐丽红, 左国民. 过氧化氢/磷钼酸体系的催化机制及对苯胺的降解效果[J]. 环境工程学报, 2022, 16(3): 867-874. doi: 10.12030/j.cjee.202111068 |
| |
| 作者姓名: | 秦汉强 肖博仁 杨金星 袁冬冬 齐丽红 左国民 |
| |
| 作者单位: | 中国人民解放军陆军防化学院,北京 102205 |
| |
| 基金项目: | 国家重点研发计划项目(2016YFC0801303) |
| |
| 摘 要: | 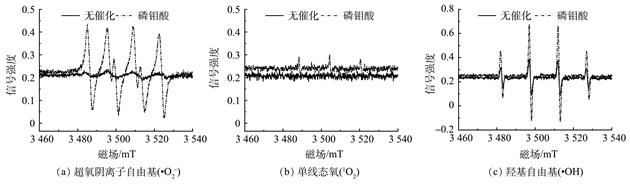
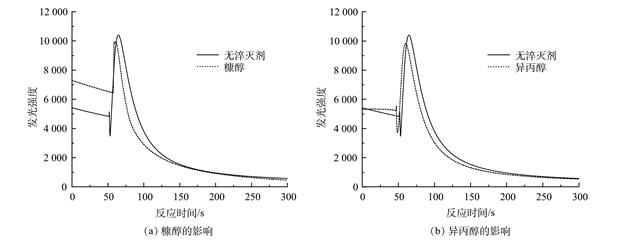
以苯胺为目标污染物,通过苯胺的降解实验从3类6种过氧化氢催化剂中筛选出催化效果较好的杂多酸催化剂磷钼酸(PMA)。利用氧化还原电位测定法、电子顺磁共振波谱法、化学发光法以及拉曼光谱法分析了H2O2/PMA催化体系的催化机制,初步推测PMA催化H2O2生成高活性的[Mo(OO)2]*和[Mo(OOH)2]*中间体。同时,考察了PMA用量、pH以及苯胺与活性氧的摩尔比对苯胺降解效果的影响,获得了H2O2/PMA体系最佳反应条件。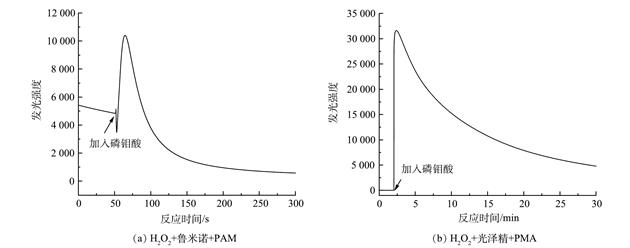
当H2O2和PMA质量分数分别为1%和0.365‰、溶液pH为4,在1 min内对4 mg·mL−1苯胺的降解率可达98%以上。通过气相色谱质谱联用仪(GC/MS)、液相色谱质谱联用仪(LC/MS)和离子色谱(IC)等仪器分析方法检测确定苯胺的降解产物,推测其在H2O2/PMA催化体系的降解途径主要以N、C原子的氧化和聚合反应为主。
|
| 关 键 词: | 过氧化氢 磷钼酸 苯胺 催化机制 降解途径 |
| 收稿时间: | 2021-11-11 |
|
| 点击此处可从《环境工程学报》浏览原始摘要信息 |
|
点击此处可从《环境工程学报》下载免费的PDF全文 |
|



