| 不同厌氧发酵系统在造纸废水处理中的应用 |
| |
| 引用本文: | 祁梦娇, 赵伟仲, 周艺璇, 夏大平, 孙长彦. 不同厌氧发酵系统在造纸废水处理中的应用[J]. 环境工程学报, 2022, 16(7): 2416-2424. doi: 10.12030/j.cjee.202112108 |
| |
| 作者姓名: | 祁梦娇 赵伟仲 周艺璇 夏大平 孙长彦 |
| |
| 作者单位: | 1.河南理工大学资源环境学院,焦作 454000; 2.河南理工大学能源科学与工程学院,焦作 454000 |
| |
| 基金项目: | 国家自然科学基金面上项目(42072193);河南省优秀青年科学基金项目(202300410168) |
| |
| 摘 要: | 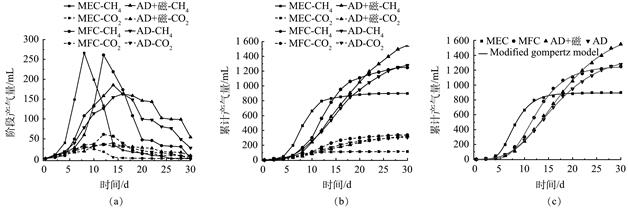
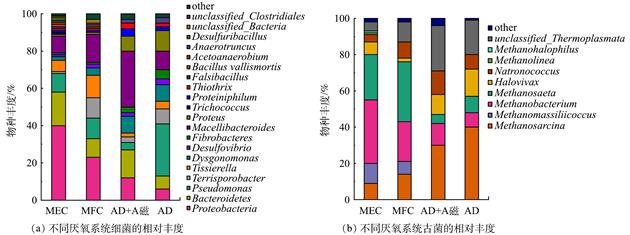
在“碳达峰和碳中和”目标下寻求高效处理造纸废水的方法尤为迫切。以某造纸厂的废水为研究对象,利用不同的厌氧发酵系统对其进行微生物降解,分别对厌氧发酵过程中的生物甲烷组分、液体组分、液体DOM、微生物群落结构进行了测定和分析,优化了处理系统。结果表明:不同厌氧发酵系统对废水中各组分降解去除能力依次为MEC-AD>MFC-AD>AD+磁铁矿>AD;MEC-AD处理造纸废水具有高效性,可促使生物甲烷高峰期相对AD提前8 d,SCOD、TP和NH4+-N去除率分别达到了77.79%、86.73%和75.98%,废水DOM中酪氨酸类蛋白质、色氨酸类蛋白质和溶解性微生物的含量显著降低,生物甲烷高峰期菌群的优势菌属为Proteobacteria、Bacteroidetes。
|
| 关 键 词: | 厌氧发酵 造纸废水 微生物电解池 微生物燃料电池 纳米磁铁矿 |
| 收稿时间: | 2021-12-15 |
|
| 点击此处可从《环境工程学报》浏览原始摘要信息 |
|
点击此处可从《环境工程学报》下载免费的PDF全文 |
|


