| 一株新型Kerstersia gyiorum 菌株CY-2对 Cr(VI) 的还原性能 |
| |
| 引用本文: | 游胜雄, 王义安, 林华, 李唐铭, 柏家欢, 赖才星. 一株新型Kerstersia gyiorum 菌株CY-2对 Cr(VI) 的还原性能[J]. 环境工程学报, 2023, 17(12): 4096-4106. doi: 10.12030/j.cjee.202307038 |
| |
| 作者姓名: | 游胜雄 王义安 林华 李唐铭 柏家欢 赖才星 |
| |
| 作者单位: | 1.桂林理工大学环境科学与工程学院,桂林 541000;; 2.桂林理工大学,广西岩溶地区水污染控制与用水安全保障协同创新中心,桂林 541000;; 3.井冈山大学生命科学学院,吉安 343000 |
| |
| 基金项目: | 国家自然科学面上基金资助项目(52070051, 52170154);广西科技计划项目(2020GXNSFAA297256);广西高等学校高水平创新团队及卓越学者计划资助(桂财教函[2018]319);广西八桂学者和特聘专家项目;井冈山大学(自然科学)博士科研启动项目(JZB2307) |
| |
| 摘 要: | 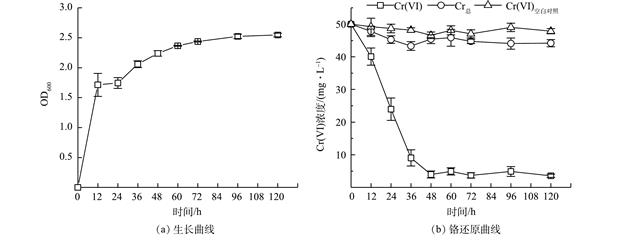
为探究李氏禾人工湿地-微生物燃料电池中铬还原菌与Cr(Ⅵ)的相互作用关系,从中筛选一株具有Cr(VI)还原能力的菌株CY-2,并对该菌还原Cr(VI)的特性和机制进行了探究。通过16S rRNA基因序列鉴定,该菌CY-2为Kerstersia gyiorum (OQ773627),其对Cr(VI)的最低抑制浓度为300 mg·L−1;在较宽的pH(4.0~9.0)、温度(27~52 ℃)和接种量(1%~20%)内还原Cr(VI);并在pH=6.0、37 ℃和10%接种量下,该菌在36 h内对50 mg·L−1 Cr(VI)的还原率为100%,对100、150、200和250 mg·L−1 的Cr(VI)在120 h内的还原率分别为62%、42%、25%和16%。此外,菌株CY-2对Mg2+、Mn2+、Cd2+、Cu2+、Co2+、Ni2+和Zn2+具有高耐受性,对呋喃唑酮、利福平和甲硝唑抗生素表现出耐药性,而对其他抗生素表现出敏感性。
SEM-EDX和FTIR表征结果表明,菌株CY-2不对铬进行生物吸附;铬的存在导致了细菌细胞表面官能团的变化,并使含硫酸盐分子减少,从而该菌可能通过还原、生物累积和外排等机制有效还原铬。以上结果表明所筛选出的菌株CY-2在铬污染场地的有效生物修复中具有潜在的应用价值。

|
| 关 键 词: | 铬还原 Kerstersia gyiorum 生物修复 还原机制 |
| 收稿时间: | 2023-07-10 |
|
| 点击此处可从《环境工程学报》浏览原始摘要信息 |
|
点击此处可从《环境工程学报》下载免费的PDF全文 |
|



