| 不同生境氨氮浓度及悬浮污泥对厌氧氨氧化生物膜特性的协同影响 |
| |
| 引用本文: | 杨慎华, 侯锋, 庞洪涛, 江乐勇, 孙事昊, 张璐晶, 彭永臻. 不同生境氨氮浓度及悬浮污泥对厌氧氨氧化生物膜特性的协同影响[J]. 环境工程学报, 2024, 18(1): 121-129. doi: 10.12030/j.cjee.202309001 |
| |
| 作者姓名: | 杨慎华 侯锋 庞洪涛 江乐勇 孙事昊 张璐晶 彭永臻 |
| |
| 作者单位: | 1.北京工业大学城镇污水深度处理与资源化利用技术国家工程实验室,北京 100124;; 2.信开环境投资有限公司,北京 101100 |
| |
| 基金项目: | 国家重点研发计划项目(2021YFC3200605) |
| |
| 摘 要: | 
生物膜技术是厌氧氨氧化工艺应用的关键,但关于不同生境氨氮浓度和悬浮污泥协同作用下形成的生物膜特性鲜有报道。本研究在推流式固定生物膜-活性污泥反应器中,发现在高氨氮浓度下生长的生物膜具有较高的污泥量和厚度,但低氨氮浓度生长的生物膜具有更高的厌氧氨氧化菌丰度((4.91±0.65)×109 拷贝数·g−1,P<0.05)和厌氧氨氧化比活性(6.53 mg·(g·h)−1)。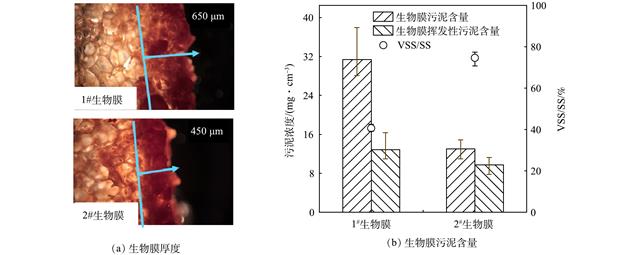
高通量分析结果表明,Candidatus Brocadia是生物膜和悬浮污泥中主要的厌氧氨氧化菌,在两类生物膜上的丰度未有显著差异;在低氨氮浓度生物膜中Candidatus Jettenia的相对丰度显著高于高氨氮浓度的生物膜,但Candidatus Kuenenia的丰度则相反。综合分析发现,厌氧氨氧化菌种的附着生长与悬浮污泥群落多样性的初始定殖有关,而低丰度菌种的分布则受不同生境的影响,该结果表明不同氨氮浓度和悬浮污泥类型的选择对生物膜的协同影响不可忽略。

|
| 关 键 词: | 短程硝化厌氧氨氧化 生物膜 氨氮浓度 悬浮污泥 微生物群落 |
| 收稿时间: | 2023-09-01 |
|
| 点击此处可从《环境工程学报》浏览原始摘要信息 |
|
点击此处可从《环境工程学报》下载免费的PDF全文 |
|



