| 基于月排放数据的北京3座区级污水处理厂年碳排放特征 |
| |
| 引用本文: | 何秋杭, 陈奕彤, 乔金岩, 张桐, 肖琪钦, 金正宇. 基于月排放数据的北京3座区级污水处理厂年碳排放特征[J]. 环境工程学报, 2023, 17(9): 2827-2840. doi: 10.12030/j.cjee.202308066 |
| |
| 作者姓名: | 何秋杭 陈奕彤 乔金岩 张桐 肖琪钦 金正宇 |
| |
| 作者单位: | 1.中央民族大学生命与环境科学学院,民族地区生态环境国家民委重点实验室,北京 100081;; 2.北京市市政工程设计研究总院有限公司,北京 100089 |
| |
| 基金项目: | 国家自然科学基金资助项目 (51608298) ;环境模拟与污染控制国家重点联合实验室开放课题 (19K06ESPCT) ;中央民族大学青年教师科研能力提升项目 (2022QNPY60) |
| |
| 摘 要: | 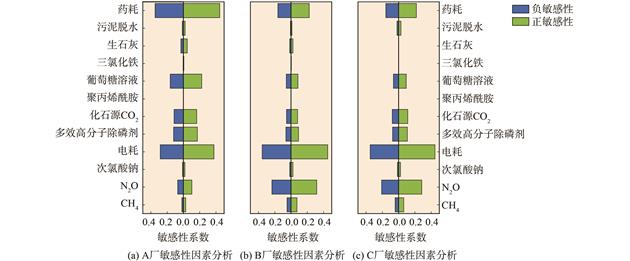
以3座北京市某区代表性区级污水处理厂为研究对象,综合《城镇水务系统碳核算与减排路径技术指南》、《污水处理厂低碳运行评价技术规范》和《IPCC 2006 年国家温室气体清单指南 2019 修订版》碳排放核算方法,采用定量统计、相关性分析及敏感性分析等手段对污水处理厂正常运行状态下碳排放核算和影响因素进行特征分析和规律识别,并提出针对性减排路径建议。结果表明:C厂C-TECH工艺的吨水碳排放强度为三厂最低1.35 kg CO2eq·m−3,处于我国较低水平,接近“双碳”目标要求;而B厂改良SBR工艺的单位污染去除碳排放强度较小,其COD碳排放强度为3.16 t CO2eq·t−1,TN碳排放强度为36.44 t CO2eq)·t−1,TP碳排放强度为176.69 t CO2eq·t−1,处于我国中上水平,从效能角度更接近“双碳”目标要求。不同工艺产生的温室气体、进水水质波动及用电消耗导致三厂碳排放强度上存在差异,但各工艺的主排碳因子均为间接碳排放 (A厂、B厂和C厂中分别占73%、59%和59%) ,间接碳排放的主贡献因子为电力消耗 (A厂、B厂和C厂中分别占33%、40%和40%) 。相关性分析发现,各水厂碳排放强度还与N2O造成的直接碳排放有较大相关性,3座水厂年排放N2O 2.48×104 t CO2eq,A厂、B厂和C厂中相关性系数值分别达到0.68、0.87、0.66。敏感性分析表明,整体碳排放强度对电力消耗、N2O排放和药耗的变化更为敏感,药耗中葡萄糖溶液和多效高分子除磷剂对碳排放强度影响较大。以上结果表明,北京区级污水处理厂应从优化曝气系统、水泵效能等节电措施和调整水厂加药模式等节药措施上实现减排。
|
| 关 键 词: | 碳排放核算 北京污水处理厂 电力消耗 相关性分析 敏感性分析 |
| 收稿时间: | 2023-08-19 |
|
| 点击此处可从《环境工程学报》浏览原始摘要信息 |
|
点击此处可从《环境工程学报》下载免费的PDF全文 |
|

