| 不同有机物对含藻水体混凝效果和絮体特性的影响 |
| |
| 引用本文: | 岳佳妮, 肖峰, 李一鸣. 不同有机物对含藻水体混凝效果和絮体特性的影响[J]. 环境工程学报, 2023, 17(10): 3333-3341. doi: 10.12030/j.cjee.202308012 |
| |
| 作者姓名: | 岳佳妮 肖峰 李一鸣 |
| |
| 作者单位: | 1.沈阳环境科学研究院,沈阳 110167;; 2.华北电力大学,北京 102206 |
| |
| 摘 要: | 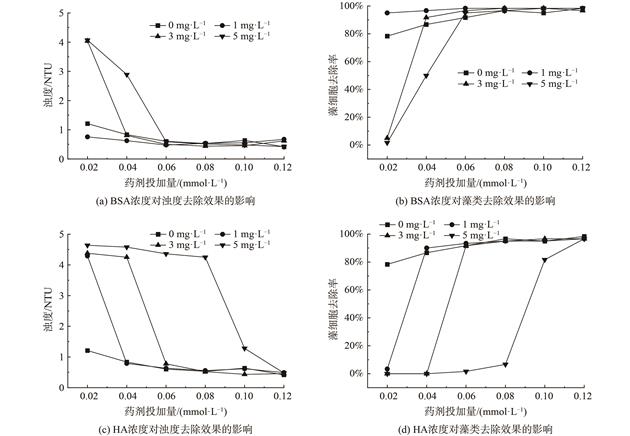
为了解不同有机物对含藻水体混凝过程的影响,以含铜绿微囊藻水体作为实验对象,考察牛血清蛋白(BSA)和腐殖酸(HA)2种有机物及其质量浓度对含藻水体浊度、藻类有机物的去除效果以及絮体形成、破碎、再絮凝的影响。结果表明,少量的BSA对混凝反应起促进作用,当BSA的投加量超过1 mg·L−1转为抑制作用,因为投加量升高时,BSA抢占混凝剂活性位点,抑制混凝反应。HA不利于混凝反应的进行,因为HA中的官能团优先与混凝剂结合,从而导致混凝效果变差。提高混凝药剂投加量可缓解有机物质量浓度增加对混凝效果的影响。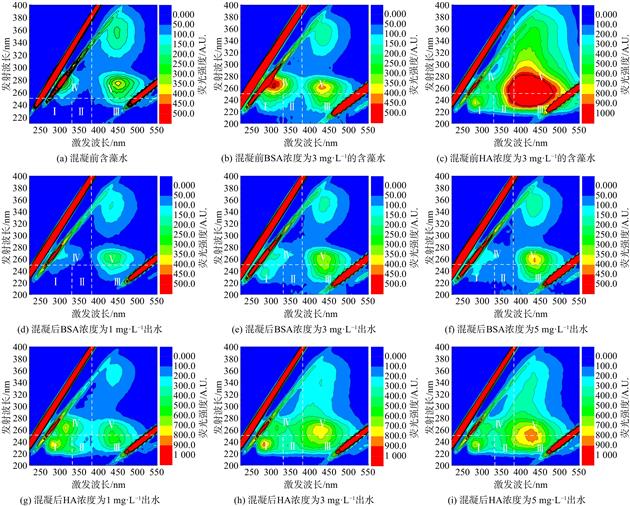
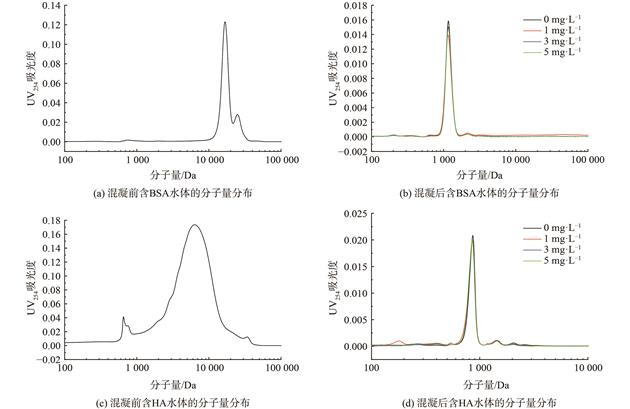
当BSA投加量为5 mg·L−1,PACl投加量为0.06 mmol·L−1时,能达到出水浊度小于1 NTU,藻细胞去除率大于90 %的混凝效果,HA添加量为5 mg·L−1,PACl投加量为0.12 mmol·L−1时,也能达到相同的混凝效果。混凝更容易去除分子质量较大的BSA和HA,而对小分子亲水性有机物的去处效果较差,如藻类有机物或HA中小分子有机物。少量的BSA和HA增加了混凝絮体的生成速率和初始粒径。本研究结果可为天然水体混凝除藻工艺优化运行提供参考。
|
| 关 键 词: | 水源水质 有机物 混凝 铜绿微囊藻 絮体特性 |
| 收稿时间: | 2023-08-04 |
|
| 点击此处可从《环境工程学报》浏览原始摘要信息 |
|
点击此处可从《环境工程学报》下载免费的PDF全文 |
|



