| Ce-ZnO/AC在真空紫外下催化降解对二甲苯废气 |
| |
| 引用本文: | 凌昊, 孟捷, 陶进国, 罗鹏飞, 赵鹏, 宋万康, 成卓韦. Ce-ZnO/AC在真空紫外下催化降解对二甲苯废气[J]. 环境工程学报, 2020, 14(11): 3092-3101. doi: 10.12030/j.cjee.202001034 |
| |
| 作者姓名: | 凌昊 孟捷 陶进国 罗鹏飞 赵鹏 宋万康 成卓韦 |
| |
| 作者单位: | 1.浙江工业大学环境学院,杭州 310032; 2.浙江泷赢环境科技有限公司,杭州 310012 |
| |
| 基金项目: | 国家重点研发计划资助项目(2018YFC0214100);浙江省自然科学基金重点项目(LZ17E080001);浙江工业大学省属高校基本科研业务费项目(RF-A2019011) |
| |
| 摘 要: | 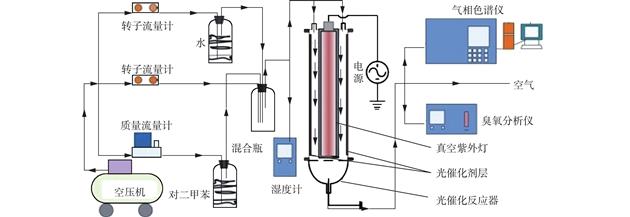
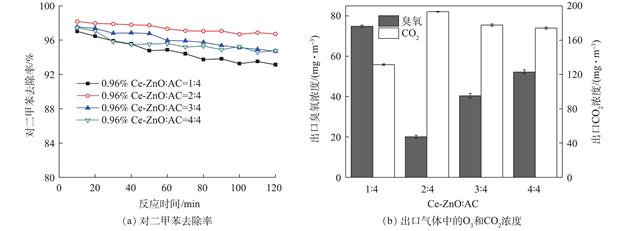
将Ce掺杂ZnO光催化剂通过负载活性炭(AC)的方式制备Ce-ZnO/AC吸附-催化复合材料,并以对二甲苯为典型挥发性有机污染物(VOC),研究其在真空紫外体系中光催化转化性能.结果 表明:活性炭的负载能有效提高臭氧的利用效率,强化对二甲苯的去除率和矿化率;当Ce-ZnO与活性炭的负载比例为1∶2时,复合材料的光催化性.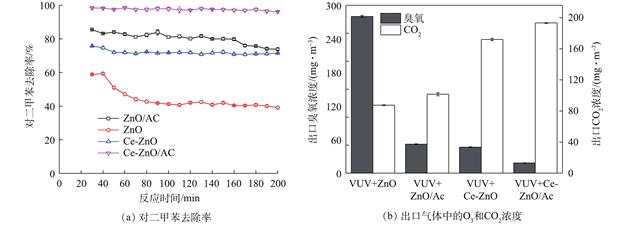
..
|
| 关 键 词: | 光催化 活性炭 对二甲苯降解 真空紫外 |
| 收稿时间: | 2020-01-07 |
|
| 点击此处可从《环境工程学报》浏览原始摘要信息 |
|
点击此处可从《环境工程学报》下载免费的PDF全文 |
|



