| 不同碳源下缺氧/好氧连续流系统生物除磷效果及其机理 |
| |
| 引用本文: | 王骞, 袁林江, 陈希, 魏萍, 霍小爱, 孟元. 不同碳源下缺氧/好氧连续流系统生物除磷效果及其机理[J]. 环境工程学报, 2021, 15(3): 954-961. doi: 10.12030/j.cjee.202008183 |
| |
| 作者姓名: | 王骞 袁林江 陈希 魏萍 霍小爱 孟元 |
| |
| 作者单位: | 1.西北水资源与环境生态教育部重点实验室,西安 710055; 2.陕西省环境工程重点实验室,西安 710055; 3.西安建筑科技大学环境与市政工程学院,西安 710055; 4.西安工程大学城市规划与市政工程学院,西安 710048 |
| |
| 摘 要: | 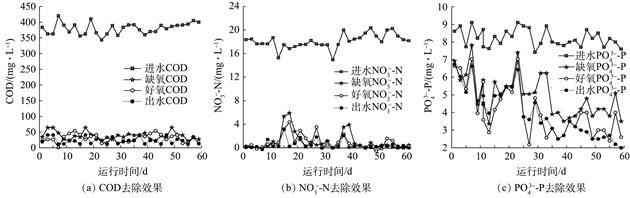
为了考察前期发现的以淀粉为唯一碳源、缺氧好氧生物脱氮系统对含多种有机物的废水中磷的脱除,在以淀粉为唯一碳源、已能稳定生物除磷(除磷率达72%)的缺氧好氧连续流生物脱氮系统中,改变进水碳源组成及浓度,测定了系统对磷去除的变化、分析了系统除磷与进水碳源的关系.结果 表明,在进水中淀粉浓度保持为400 mg·L-1(以COD.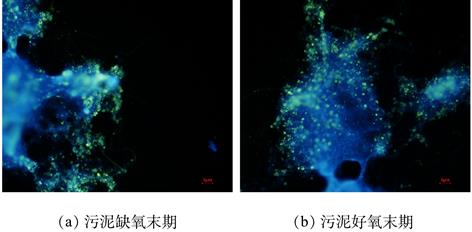
..

|
| 关 键 词: | 缺氧好氧连续流系统 生物除磷 产乳酸发酵菌 糖原 乳酸 |
| 收稿时间: | 2020-08-19 |
| 本文献已被 万方数据 等数据库收录! |
| 点击此处可从《环境工程学报》浏览原始摘要信息 |
|
点击此处可从《环境工程学报》下载免费的PDF全文 |
|



