| 单井捕获地下水污染羽的优化方法 |
| |
| 引用本文: | 宫志强, 刘明柱, 刘伟江, 田西昭, 康阳, 李书焱, 王丽, 陈坚. 单井捕获地下水污染羽的优化方法[J]. 环境工程学报, 2019, 13(10): 2468-2474. doi: 10.12030/j.cjee.201812028 |
| |
| 作者姓名: | 宫志强 刘明柱 刘伟江 田西昭 康阳 李书焱 王丽 陈坚 |
| |
| 作者单位: | 1.生态环境部环境规划院,长江经济带生态环境联合研究中心,北京 100012; 2.河北省地质环境监测院,河北省地质资源环境监测与保护重点实验室,石家庄 050021; 3.中国地质大学(北京)水资源与环境学院,北京 100083 |
| |
| 基金项目: | 国家自然科学基金;水体污染控制与治理科技重大专项 |
| |
| 摘 要: | 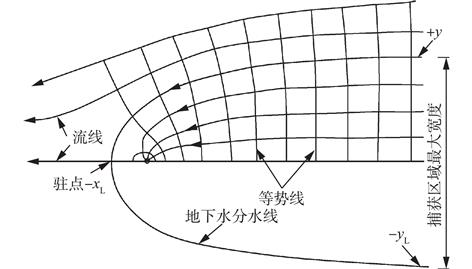
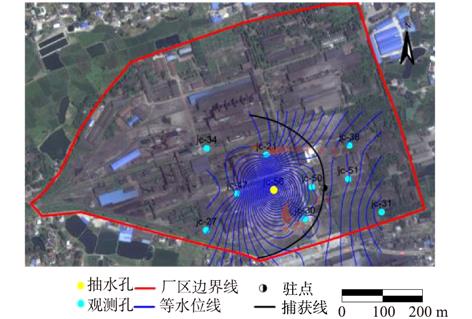
针对不同抽水井捕获半径及驻点获取方法存在局限性和误差的问题,以潜水、承压水2个类型污染场地为例,分别采用实测法、解析解公式法、数值模拟法3种方法计算单井捕获半径及驻点值;通过对比分析,研究了不同条件下3种方法的局限性及精确度;探讨了不同类型污染场地获取捕获半径及驻点的最适宜方法。结果表明:对于承压水类型,解析解计算值与实际观测值误差较小,为3.2%;对于水位降深相对于含水层厚度不可忽略的潜水类型,解析解计算值与实际观测值误差较大,为80.7%;在充分掌握水文地质条件时,数值模型模拟结果与实际观测误差值不超过10%。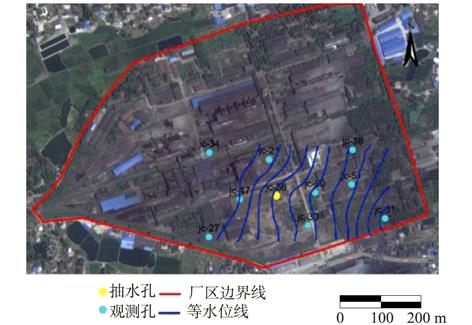
因此,当场地水文地质情况符合解析解公式假设条件时,可采用解析解公式法获取单井捕获半径及驻点,否则须利用数值模拟方法或实测法获取相关参数。研究成果为不同类型污染场地选择合适方法获取捕获半径及驻点提供了参考。
|
| 关 键 词: | 抽水实验实测法 解析解公式法 数值模拟 捕获半径 驻点 最优 |
| 收稿时间: | 2018-12-04 |
| 本文献已被 CNKI 万方数据 等数据库收录! |
| 点击此处可从《环境工程学报》浏览原始摘要信息 |
|
点击此处可从《环境工程学报》下载免费的PDF全文 |
|



